How To Design A Food Production Line
1. Introduction
Importance of a Well-Designed Food Production Line
A well-designed food production line ensures efficiency, product quality, and safety. It minimizes production costs, reduces waste, and helps meet regulatory requirements.
Overview of Key Considerations
Key considerations include understanding the production process, selecting appropriate equipment, planning the layout, ensuring food safety, integrating technology, staffing, maintaining quality control, and considering sustainability.
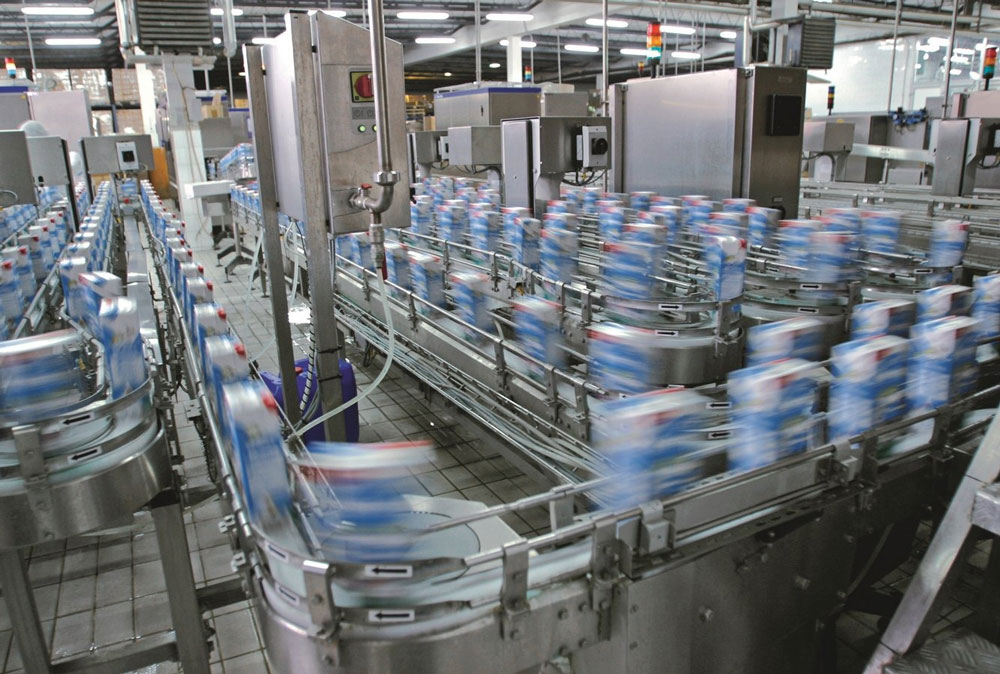

2. Understanding the Production Process
Defining the Product
Start by defining the product you will be producing. This includes understanding the ingredients, desired shelf life, packaging requirements, and any specific characteristics.
Mapping Out the Production Stages
Break down the production process into distinct stages, such as raw material handling, processing, cooking or baking, cooling, packaging, and storage. Create a detailed flowchart to visualize the process.
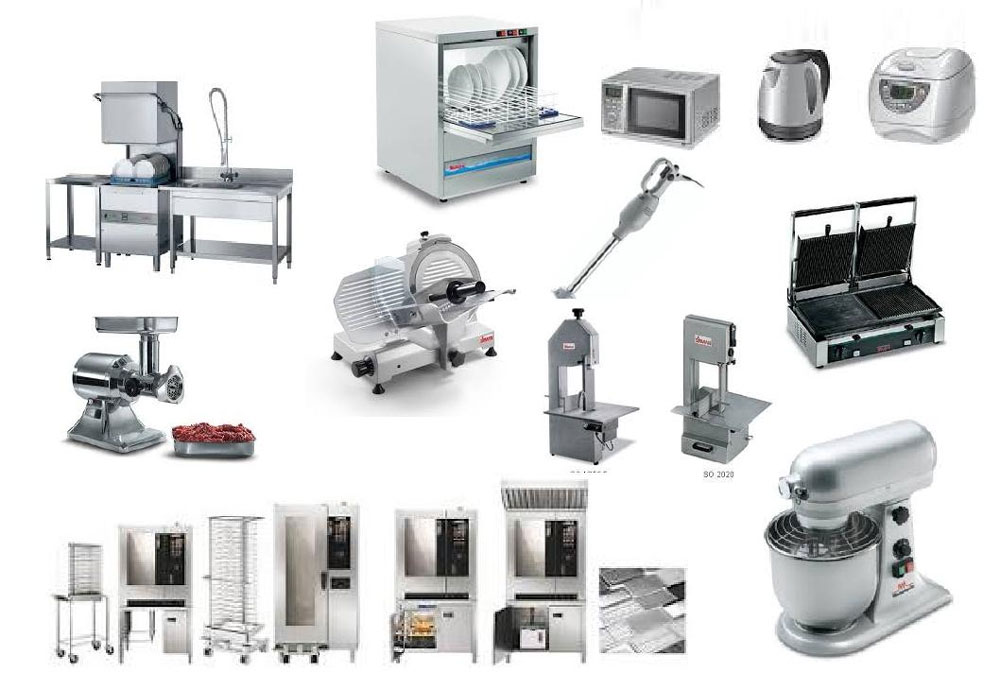

3. Equipment Selection
Criteria for Selecting Equipment
Select equipment based on:
- Capacity requirements
- Compatibility with the product
- Ease of cleaning and maintenance
- Compliance with safety standards
- Energy efficiency
Types of Equipment Needed
Common equipment includes mixers, ovens, conveyors, filling machines, packaging machines, and refrigeration units. The specific equipment depends on the product and production volume.

4. Layout Planning
Principles of Layout Design
Design the layout to minimize movement and handling of materials, ensuring a smooth flow from raw materials to finished products. Consider space for storage, processing, packaging, and staff movement.
Workflow Optimization
Optimize workflow by arranging equipment in a logical sequence. Implement lean manufacturing principles to reduce waste and improve efficiency.
5. Food Safety and Compliance
Hygiene and Sanitation Standards
Design the production line to facilitate easy cleaning and maintenance. Use materials that are resistant to corrosion and easy to sanitize. Implement strict hygiene protocols to prevent contamination.
Regulatory Requirements
Ensure compliance with local and international food safety regulations, such as HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points), FDA (Food and Drug Administration), and ISO (International Organization for Standardization) standards.
6. Automation and Technology Integration
Benefits of Automation
Automation increases production speed, consistency, and accuracy. It reduces labor costs and the potential for human error.
Implementing Technology Solutions
Integrate technologies such as sensors, IoT (Internet of Things) devices, and automated quality control systems. Use software for production planning, inventory management, and real-time monitoring.
7. Staffing and Training
Staffing Requirements
Determine the number of staff needed based on the production volume and complexity of the process. Assign roles and responsibilities clearly.
Training Programs
Develop comprehensive training programs covering equipment operation, safety protocols, hygiene practices, and emergency procedures.
8. Quality Control and Testing
Quality Control Measures
Implement quality control measures at each stage of the production process. Use statistical process control (SPC) to monitor and control quality.
Testing Protocols
Conduct regular testing for product consistency, safety, and compliance. Use laboratory tests, sensory evaluations, and shelf-life studies.
9. Sustainability Considerations
Eco-Friendly Practices
Adopt eco-friendly practices such as energy-efficient equipment, renewable energy sources, and sustainable sourcing of raw materials.
Waste Management
Implement waste management strategies to reduce, reuse, and recycle production waste. Consider composting organic waste and recycling packaging materials.
10. Case Study or Example
Real-World Application
Provide an example of a successfully designed food production line, highlighting the key aspects of design, implementation, and results achieved.
This guide outlines the steps and considerations for designing a food production line. Each section can be expanded based on specific needs and detailed further to create a comprehensive plan. If you need more detailed information on any particular section or help with creating specific diagrams or templates, feel free to ask!
Must-Read Blogs For Chain Restaurants Owner






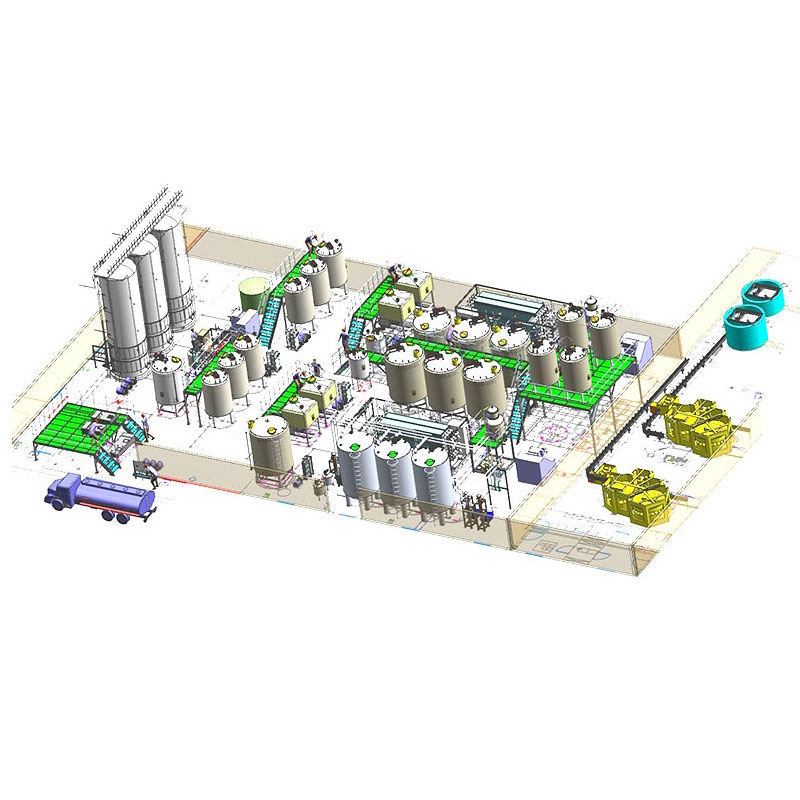



 Meat Canned Food Production Line
Meat Canned Food Production Line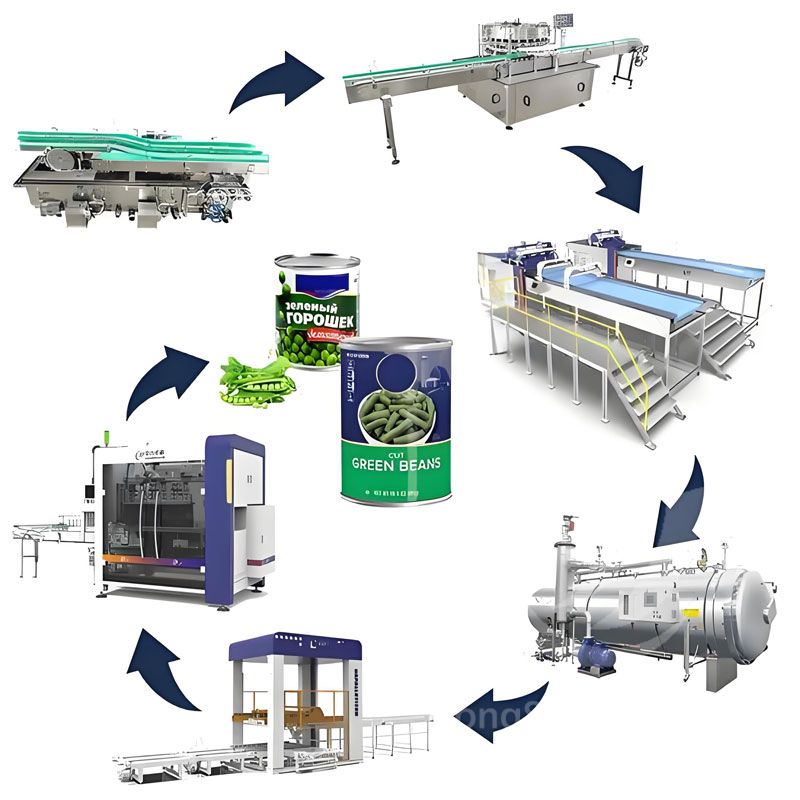 Green Bean Canned Food Production Line
Green Bean Canned Food Production Line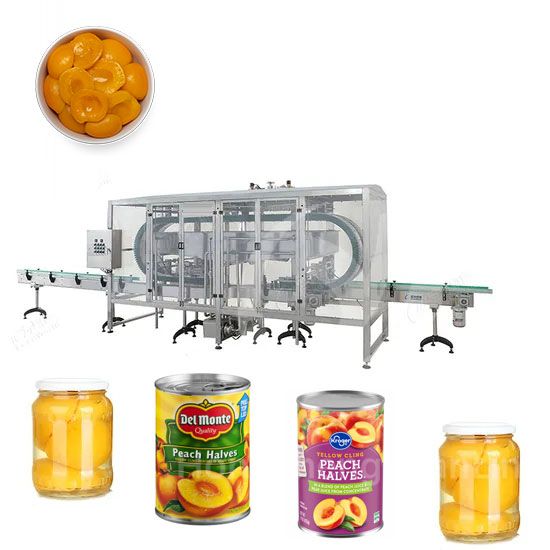 Peach Canned Food Production Line
Peach Canned Food Production Line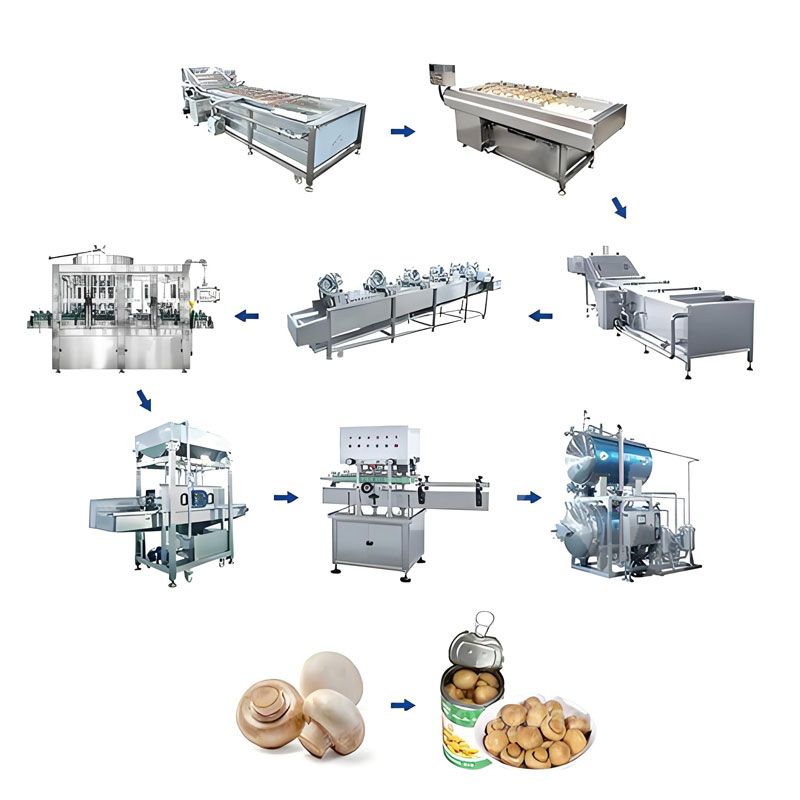 Edible Mushroom Canned Food Production Line
Edible Mushroom Canned Food Production Line
Ready to Get Started?