What Are The Steps Of Meat Processing?
Meat processing is a complex and vital industry that transforms animal carcasses into a variety of meat products ready for consumption. Whether it's beef, pork, lamb, or poultry, the process involves several meticulous steps to ensure food safety, quality, and flavor. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate world of meat processing, detailing each step, techniques employed, and the significance of this industry in meeting global food demands.
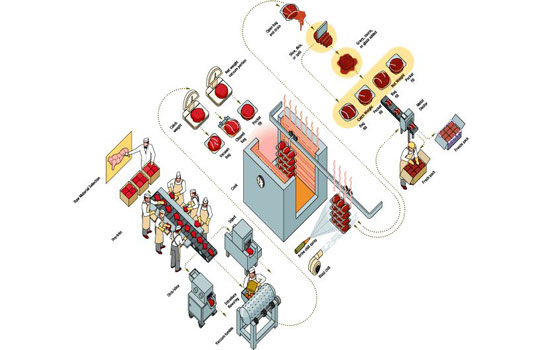
Introduction to Meat Processing
Meat processing encompasses the entire journey from slaughter to packaging, ensuring that meat products are safe, flavorful, and nutritious for consumers. It involves a series of steps that adhere to strict hygiene and quality standards to prevent contamination and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Steps of Meat Processing
Step 1: Slaughtering
The first step in meat processing begins with the humane slaughtering of animals in accredited facilities. This step is critical for minimizing stress to animals and ensuring the safety and quality of the meat. Modern facilities employ humane handling practices and stunning techniques to minimize pain and distress.
Step 2: Skinning and Dehairing
After slaughter, the animal carcass undergoes skinning and dehairing processes. Skinning removes the outer layer of skin, while dehairing is specific to pigs and involves removing hair from the carcass. These steps are crucial to prepare the carcass for further processing.
Step 3: Evisceration and Gutting
Evisceration involves removing the internal organs (viscera) from the carcass. This step is carried out meticulously to prevent contamination of the meat with digestive fluids and bacteria from the intestines. Proper hygiene and sanitation practices are essential during evisceration to ensure food safety.
Step 4: Splitting and Quartering
Large animal carcasses such as beef and lamb are often split or quartered into smaller, manageable sections. This facilitates further processing and allows for specific cuts of meat to be prepared according to market demand and consumer preferences.
Step 5: Washing and Chilling
After initial processing, carcasses are washed thoroughly to remove residual blood, dirt, and bacteria. Chilling the carcasses rapidly to temperatures below 40°F (4°C) is crucial to inhibit bacterial growth and maintain meat quality. Proper chilling also enhances the tenderness and flavor of the meat.
Step 6: Cutting and Boning
Meat is then cut and boned according to specific requirements. Skilled butchers and meat processors use various cutting techniques to prepare primal cuts such as ribs, loins, and shoulders. Boning involves removing bones from meat cuts to produce boneless products such as steaks and fillets.
Step 7: Grinding and Mixing (Optional)
Ground meat products such as ground beef and sausage are prepared by grinding meat trimmings and mixing them with spices, seasonings, and other ingredients. This step allows for the creation of diverse meat products tailored to consumer preferences.
Step 8: Forming and Shaping (Optional)
Some meat products undergo forming and shaping processes to create uniform shapes and sizes. This is common in the production of burger patties, meatballs, and nuggets. Forming machines ensure consistency in product shape and weight.
Step 9: Cooking, Smoking, or Curing (Optional)
Certain meat products undergo additional processing methods such as cooking, smoking, or curing to enhance flavor, texture, and shelf life. Smoking imparts a distinct flavor, while curing with salt and other ingredients preserves the meat and develops unique flavors.
Step 10: Packaging and Storage
The final step in meat processing involves packaging the meat products in vacuum-sealed packages or modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) to extend shelf life and maintain freshness. Proper labeling with nutritional information, expiration dates, and handling instructions is essential for consumer safety.
Techniques Employed in Meat Processing
- Hygiene and Sanitation: Strict hygiene practices are paramount throughout meat processing to prevent contamination and ensure food safety.
- Quality Control: Quality control measures are implemented at every stage to monitor meat quality, appearance, and safety standards.
- Temperature Control: Maintaining precise temperatures during processing, chilling, and storage is critical to prevent bacterial growth and maintain meat quality.
- Automation: Modern meat processing facilities employ advanced machinery and automation to improve efficiency, consistency, and safety.
Importance of Meat Processing
Meat processing plays a crucial role in meeting global food demands by transforming perishable animal carcasses into safe, nutritious, and convenient meat products. Key benefits include:
- Food Safety: Rigorous processing standards ensure that meat products are safe for consumption.
- Nutritional Value: Processing methods can enhance the digestibility and nutritional content of meat products.
- Consumer Convenience: Diverse meat products cater to consumer preferences and culinary traditions.
- Economic Contribution: Meat processing supports livelihoods in agriculture, food manufacturing, and distribution sectors globally.
Conclusion
Meat processing is a sophisticated and indispensable industry that transforms raw animal carcasses into a wide array of safe, nutritious, and flavorful meat products. Each step in the process—from slaughter to packaging—requires meticulous attention to detail, adherence to hygiene standards, and compliance with regulatory requirements to ensure consumer safety and satisfaction. By employing advanced techniques and technologies, meat processors continue to innovate and meet evolving consumer preferences while contributing significantly to global food security and economic growth.
In conclusion, meat processing is an intricate and vital industry that transforms animal carcasses into a variety of safe and nutritious meat products. Each step in the process, from slaughtering to packaging, plays a crucial role in ensuring food safety, quality, and consumer satisfaction. By adhering to stringent hygiene practices, employing advanced processing techniques, and maintaining strict quality control measures, meat processors uphold high standards and contribute to global food security and economic development.
Must-Read Blogs For Chain Restaurants Owner









 Canned Meat Production Line
Canned Meat Production Line Meat Processing Line Equipment
Meat Processing Line Equipment Cold Chain Rice Production Line
Cold Chain Rice Production Line Unmanned Intelligent Rice Production Line
Unmanned Intelligent Rice Production Line
Ready to Get Started?