Canning Production Line Cost: A Complete Guide for Food Manufacturers
1. Introduction
Investing in a canning production line is a significant step for any food processing business. Whether you produce fish, meat, vegetables, sauces, or beverages, understanding the total cost is essential for budgeting, ROI calculation, and supplier selection.
The cost of a canning line depends on factors such as automation level, production capacity, product type, and manufacturer reputation. This guide breaks down all cost components and provides insights into making a smart investment.
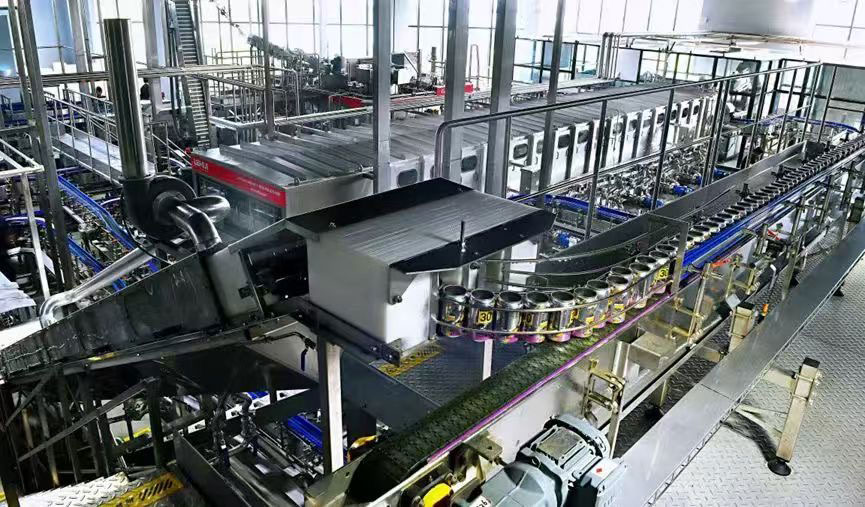

2. Key Factors Affecting Canning Production Line Cost
2.1 Production Capacity
The volume of cans you plan to produce directly affects the machinery specifications:
| Capacity | Cans/Minute | Estimated Line Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Small-Scale | 30–100 | $30,000–$80,000 |
| Medium-Scale | 200–500 | $100,000–$300,000 |
| Large Industrial | 800–2,000+ | $500,000–$1,500,000+ |
2.2 Automation Level
Semi-Automatic: Operators manually feed cans, fill, or seal. Lower cost, higher labor.
Fully Automatic: Automated feeding, filling, sealing, and labeling. Higher upfront cost but reduced labor and higher efficiency.
2.3 Product Type
Different products require specific equipment, influencing cost:
Fish and Meat: Require pre-cooking, sterilization, and precise portioning → higher cost
Vegetables and Fruits: May need blanching and peeling equipment → medium cost
Sauces and Liquids: Require piston fillers or volumetric fillers → medium to high cost
Beverages: Require aseptic filling and sterilization → high cost
2.4 Can Size and Material
Standard tinplate cans are cheaper; aluminum or specialty cans increase cost.
Larger cans require stronger sealing machines and bigger retorts.
2.5 Manufacturer and Brand
European brands (Marel, Baader, GEA): High-precision, long lifespan, higher price.
Chinese manufacturers (Qingdao Hongshengyuanlin, Zhucheng Zhongyu): Cost-effective turnkey solutions with global export experience.
3. Breakdown of Costs in a Canning Production Line
| Cost Component | Description | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Machinery | Fillers, seaming machines, retorts, conveyors | 60–70% of total cost |
| Installation & Commissioning | On-site setup, testing, calibration | 10–15% |
| Transportation | Shipping heavy machinery internationally | 5–10% |
| Training | Operator and maintenance training | 2–5% |
| Utilities & Infrastructure | Water, electricity, HVAC, factory modifications | 5–10% |
| Spare Parts & Initial Consumables | Seals, gaskets, lubricants | 2–5% |
Example: A medium-scale fish canning line costing $250,000 may allocate ~$150,000 for equipment, $25,000 for installation, $15,000 for shipping, $10,000 for training, and the rest for utilities and spare parts.
4. Cost Examples by Product
4.1 Fish Canning Line
Capacity: 5,000 cans/hour
Machinery: Automatic fish cleaning, cutting, filling, seaming, sterilization
Cost Range: $250,000–$500,000
ROI: 12–18 months depending on raw material supply and market demand
4.2 Fruit and Vegetable Canning Line
Capacity: 10,000 cans/hour
Machinery: Peeling, cutting, filling, seaming, retort sterilizer
Cost Range: $150,000–$400,000
4.3 Sauce and Paste Canning Line
Capacity: 5,000–10,000 cans/hour
Machinery: Piston fillers, seaming machines, retorts
Cost Range: $200,000–$450,000
4.4 Beverage Canning Line
Capacity: 8,000–12,000 cans/hour
Machinery: Aseptic fillers, sterilizers, conveyor system
Cost Range: $300,000–$1,000,000+
Tip: The more complex the product or stricter the sterilization requirements, the higher the cost.
5. Hidden Costs to Consider
Energy Consumption: Retorts and fillers consume high power; ensure your factory can handle load.
Water Usage: Cooling and sterilization require significant water; may need recycling systems.
Maintenance: Periodic maintenance, spare parts, and service agreements can add 5–10% annually.
Factory Modification: Retrofitting a building for line installation may involve civil works.
Regulatory Compliance: Food safety certifications (HACCP, ISO22000, FDA) may require additional testing equipment.
6. Cost-Saving Strategies
Choose modular lines: Start with small capacity and expand later.
Opt for semi-automatic lines initially if labor cost is low.
Consider local manufacturers for lower shipping costs.
Use energy-efficient machines to reduce operational cost.
Train operators in multi-tasking to reduce staff requirements.
7. Return on Investment (ROI) Considerations
ROI depends on production efficiency, labor savings, and market price.

Example:
Total equipment cost: $300,000
Annual profit increase: $100,000
Annual labor savings: $50,000
ROI = (100,000 + 50,000) ÷ 300,000 × 100% = 50% per year
High automation and efficiency reduce ROI payback time, often achieving 1–2 years for mid-scale lines.
8. Top Manufacturers for Cost-Effective Canning Lines
Chinese Manufacturers (Cost-effective options)
Qingdao Hongshengyuanlin Co., Ltd. – Turnkey fish and vegetable canning lines
Zhucheng Zhongyu Machinery – Semi-automatic and full-automatic canning systems
Shanghai Leadworld – High-speed lines for sauces and pastes
European Manufacturers (Premium quality, higher cost)
Marel (Netherlands/Iceland) – Fish and meat canning lines
Baader Group (Germany) – Advanced fish portioning and canning
GEA Group (Germany) – Multi-purpose canning solutions for vegetables and sauces
Choosing between cost-effective vs premium depends on budget, expected ROI, labor cost, and product quality requirements.
9. Small vs Large-Scale Lines: Cost Comparison
| Feature | Small-Scale | Large-Scale Industrial |
|---|---|---|
| Cans per Hour | 30–500 | 800–2,000+ |
| Initial Cost | $30,000–$80,000 | $500,000–$1,500,000+ |
| Labor Required | High | Low (automation) |
| ROI Payback | 2–3 years | 1–2 years |
| Flexibility | Easier product switch | Requires planning and setup |
10. Conclusion
The canning production line cost varies widely based on capacity, automation, product type, and manufacturer. Understanding all cost components—including equipment, installation, utilities, and maintenance—is essential for calculating ROI and planning production expansion.
Small lines are suitable for startups or limited budgets, with slower ROI.
Medium to large industrial lines offer faster ROI, higher automation, and global market compliance.
Cost-effective manufacturers in China provide turnkey solutions with competitive pricing.
Premium European brands provide high precision, long lifespan, and advanced automation.
Investing wisely in the right canning production line ensures high-quality production, reduced labor costs, compliance with international food safety standards, and long-term profitability.
Must-Read Blogs For Chain Restaurants Owner










 Cold Chain Rice Production Line
Cold Chain Rice Production Line Unmanned Intelligent Rice Production Line
Unmanned Intelligent Rice Production Line Automatic Rice Production Line
Automatic Rice Production Line
Ready to Get Started?