Investing in Canned Food Production Lines: Benefits and Key Considerations
Canned food has long been a cornerstone of global food supply chains, offering convenience, shelf stability, and nutritional value to consumers worldwide. For food processing companies aiming to enter or expand in the canned food sector, investing in a modern Canned Food Production Line is a critical strategic decision. This guide provides a detailed examination of the multifaceted considerations that enterprises must evaluate when investing in canned food production lines. It covers investment costs, expected returns, technical and operational requirements, and market prospects. Through this exhaustive analysis, enterprises will be empowered to make informed, cost-effective decisions that maximize operational efficiency and market competitiveness.
1. Overview of Canned Food Production Lines
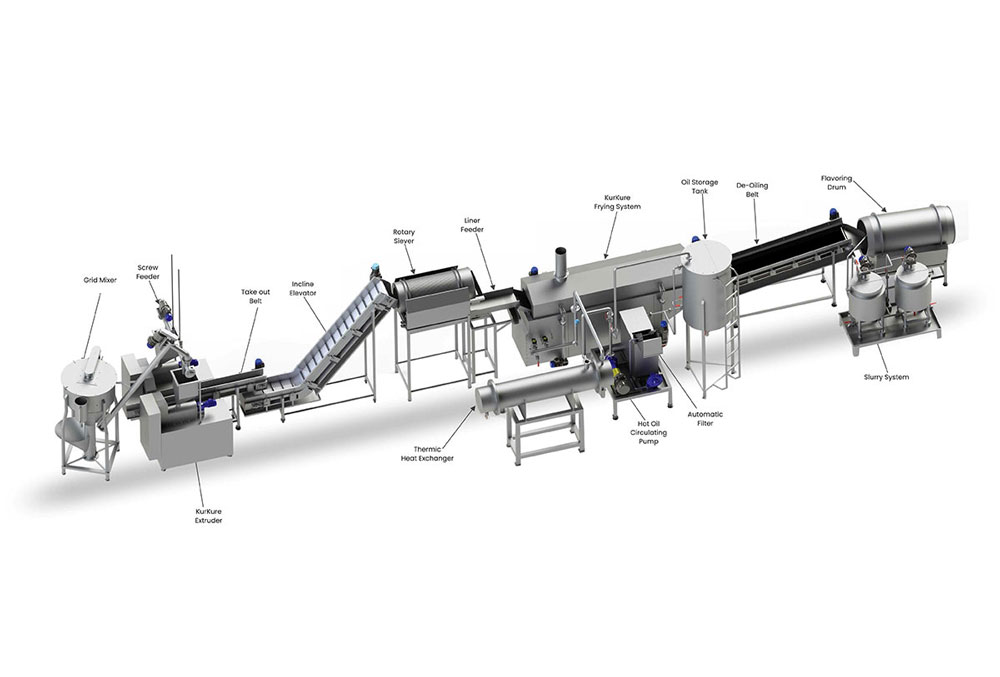
A canned food production line is a complex system integrating multiple processes including raw material preparation, cooking, filling, sealing, sterilization, labeling, and packaging. Depending on production scale and automation level, these lines can range from semi-automatic setups suitable for small batches to fully automated systems designed for high-volume continuous production.
1.1 Production Line Components
Typical equipment and process steps include:
Raw material washing and sorting machines
Cooking kettles or steam cookers
Filling machines (vacuum or piston type)
Sealing machines (double seaming for cans)
Sterilization equipment (retorts or continuous sterilizers)
Labeling and packaging machines
Conveyors and quality inspection stations
A well-designed line ensures product quality, maximizes throughput, minimizes waste, and maintains stringent food safety standards.
2. Investment Costs: Breaking Down the Budget
Investment in canned food production lines varies widely depending on automation level, production capacity, equipment quality, and customization.
2.1 Small-Scale Semi-Automated Lines
Cost Range: Approximately 500,000 to 1.5 million RMB
Target Users: Startups, niche producers, research and development pilots
Characteristics:
Manual or semi-automatic operation reducing upfront capital
Limited throughput (typically below 2 tons/day)
Suitable for artisan or specialty canned products
Pros and Cons:
Lower initial investment and simpler training requirements
Higher labor costs and limited scalability
2.2 Medium-Scale Automated Lines
Cost Range: Approximately 3 million to 15 million RMB
Target Users: Growing SMEs seeking stable production volumes
Characteristics:
Partial automation in filling, sealing, and packaging
Production capacity ranging from 2 to 10 tons/day
Enhanced production consistency and product quality
Pros and Cons:
Balance of automation and flexibility
Moderate labor and maintenance demands
Higher upfront costs compared to semi-automatic setups
2.3 Large-Scale Fully Automated Lines
Cost Range: 20 million RMB and above, potentially exceeding 100 million RMB for ultra-large customized plants
Target Users: Large enterprises and multinational food producers
Characteristics:
Fully automated workflows with integrated control systems
High throughput (10+ tons/day) with continuous operation capability
Advanced sterilization (continuous retorts), robotic handling, and smart quality control
Pros and Cons:
Maximizes efficiency and reduces per-unit costs
Requires significant capital and highly trained technical teams
Longer installation and commissioning times
3. Return on Investment (ROI): What to Expect
Determining ROI for canned food production lines involves a thorough analysis of multiple variables, including production costs, product pricing, market demand, and operational efficiency.
3.1 Key Influencing Factors
Market Demand and Product Positioning: High consumer demand or niche premium products typically accelerate ROI.
Operational Costs: Including labor, raw materials, energy consumption, and maintenance. Automated lines may reduce labor but increase maintenance complexity.
Production Efficiency: Optimized equipment utilization and minimal downtime enhance profitability.
Supply Chain Stability: Reliable raw material sourcing at competitive prices helps maintain margins.
Regulatory Compliance Costs: Meeting stringent food safety regulations can incur additional expenses but improve market acceptance.
3.2 Typical ROI Periods
Small-scale lines: 2 to 4 years
Medium-scale automated lines: 3 to 6 years
Large-scale fully automated lines: 5 to 10 years, depending on market and management
Strategic product innovation, marketing, and efficient operations shorten these timelines.
4. Technical and Operational Considerations
A canned food production line is not just an equipment purchase; it is an integrated operational system requiring ongoing technical support, maintenance, and skilled personnel.
4.1 Skilled Workforce Requirements
Operators trained in machinery control and quality assurance
Maintenance engineers with knowledge of mechanical, electrical, and automation systems
Food safety officers ensuring regulatory compliance
4.2 Maintenance and Spare Parts
Preventive maintenance schedules minimize downtime and costly breakdowns
Readily available spare parts, especially for critical components such as sealing heads and sterilizers, ensure smooth production
Suppliers offering comprehensive after-sales service contracts and remote support reduce risks
4.3 Automation and Control Systems
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) and Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI) facilitate precision control
Data collection and analysis for production optimization and traceability
Integration with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems enhances supply chain transparency
5. Market Outlook: Opportunities and Trends
5.1 Growing Consumer Demand
Urbanization and changing lifestyles continue to drive demand for convenient, shelf-stable foods. Canned products meet these needs with long shelf life, easy preparation, and nutrient preservation.
5.2 Product Innovation
Health-oriented products: Low sodium, organic, additive-free
Ethnic and gourmet canned specialties attract discerning consumers
Innovative packaging solutions improve user convenience and sustainability
5.3 Global Expansion
Emerging markets in Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America show rising canned food consumption. Export-oriented producers benefit from compliance with international standards and certifications.
6. Risk Management and Strategic Planning
To maximize investment effectiveness, companies should undertake comprehensive feasibility studies, including:
Market research and competitive analysis
Detailed cost-benefit assessments
Supplier audits and equipment quality verification
Workforce capacity evaluation and training plans
Regulatory landscape review and certification planning
7. Final Recommendations
Match production capacity and automation to current market size and growth plans
Prioritize suppliers with proven track records and strong after-sales support
Invest in staff training and food safety culture development
Plan for phased upgrades and scalability to accommodate future growth
Continuously monitor market trends and consumer preferences to innovate product lines
Conclusion
Investing in canned food production lines is a complex yet rewarding venture that requires strategic foresight, financial prudence, and operational excellence. By carefully evaluating investment scales, ROI potentials, technical requirements, and market opportunities, food enterprises can position themselves for sustainable growth in a competitive industry landscape. Proper planning and partnership with experienced equipment suppliers will be critical in translating capital investments into operational success and market leadership.
Must-Read Blogs For Chain Restaurants Owner










 Cold Chain Rice Production Line
Cold Chain Rice Production Line Unmanned Intelligent Rice Production Line
Unmanned Intelligent Rice Production Line Automatic Rice Production Line
Automatic Rice Production Line
Ready to Get Started?