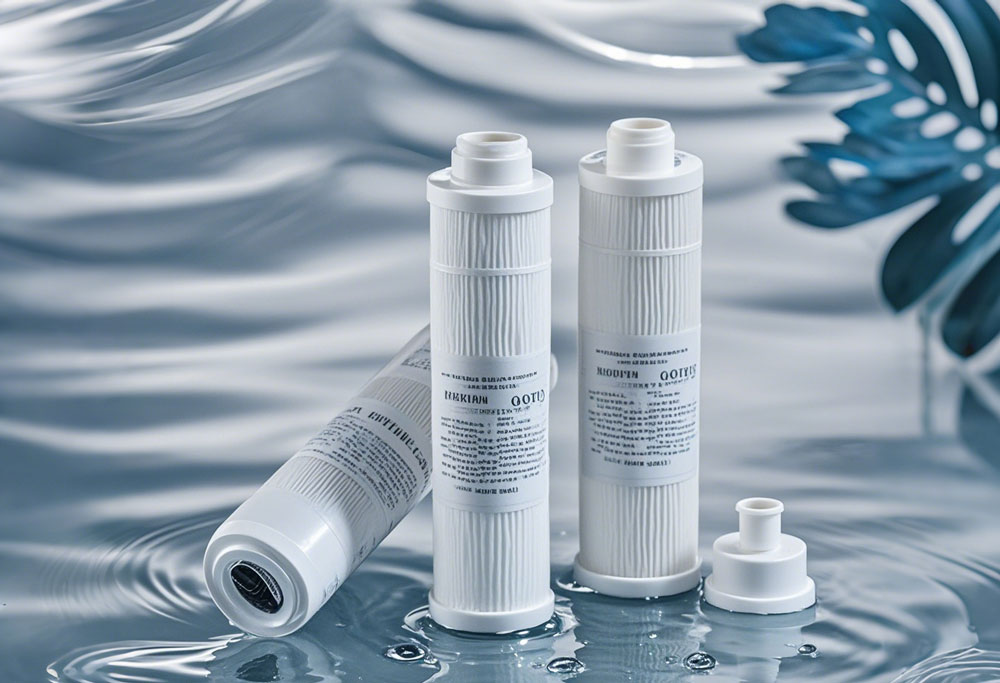

In today's world, ensuring the purity of drinking water is paramount. With a plethora of water purifier filters available, choosing the right one can be daunting. Each filter type is designed to tackle specific contaminants, and understanding their differences is crucial for making an informed decision. This comprehensive guide explores the various types of water purifier filters, their working mechanisms, pros and cons, and how to choose the right one for your home.
Water purifier filters are essential in providing clean and safe drinking water by removing contaminants and improving water quality. Here, we delve into the most common types of water filters, how they work, their benefits, and drawbacks.
How They Work: Reverse osmosis filters use a semi-permeable membrane to remove impurities from water. Water is forced through the membrane under pressure, leaving contaminants behind.
Pros:
- Removes a wide range of impurities, including heavy metals, bacteria, viruses, and dissolved solids.
- Produces high-purity water.
- Easy to maintain with simple filter replacements.
Cons:
- Wastes a significant amount of water during the filtration process.
- May remove beneficial minerals, potentially making the water acidic.
- Requires electricity to operate.
How They Work: Activated carbon filters use porous carbon material to adsorb organic compounds, chlorine, and other chemicals that cause unpleasant tastes and odors.
Pros:
- Effectively removes chlorine, odors, and bad taste.
- Inexpensive and widely available.
- Can be used in various filtration systems, such as pitcher filters, faucet filters, and under-sink filters.
Cons:
- Does not effectively remove dissolved solids, heavy metals, or microorganisms.
- Filters need to be replaced regularly to maintain effectiveness.
How They Work: UV water purifiers use ultraviolet light to kill bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms in water. Water passes through a chamber where it is exposed to UV light, which destroys the DNA structure of microorganisms.
Pros:
- Highly effective in microbial control.
- No chemical process, no residue or taste.
- Minimal maintenance required.
Cons:
- Does not remove non-biological contaminants such as heavy metals or chemicals.
- Requires electricity to operate.
- May require pre-filtration to remove sediment that can protect microorganisms from UV damage.
How They Work: Ceramic filters use porous ceramic materials to block particles, bacteria, and protozoa in the water. The ceramic material has extremely fine pores that capture larger contaminants.
Pros:
- Effective removal of bacteria and cysts.
- Long service life and easy to clean.
- No electricity required.
Cons:
- Not effective in removing viruses, chemicals, or dissolved minerals.
- May become clogged during use and requires regular cleaning.
- Slower filtration process compared to other methods.
How They Work: Distillation involves boiling water to create steam, which is then condensed back into liquid, leaving contaminants behind.
Pros:
- Removes a wide range of contaminants, including heavy metals, bacteria, and minerals.
- Provides very pure water.
Cons:
- Slow process and consumes a lot of energy.
- Removes beneficial minerals along with harmful substances.
- Distilled water may taste bland or insipid.
How They Work: Ion exchange filters soften water by replacing hardness ions (such as calcium and magnesium) with sodium or potassium ions through an ion exchange process.
Pros:
- Effectively reduces water hardness.
- Can prevent limescale buildup and extend the life of household appliances.
Cons:
- Does not remove other types of contaminants.
- Regular regeneration of the resin with salt is required.
- Sodium content of the softened water may increase.
How They Work: Alkaline water filters, also known as water ionizers, separate water into alkaline and acidic components through electrolysis.
Pros:
- Alkaline water may have a better taste due to its higher pH value.
- Some users claim health benefits from long-term consumption of alkaline water.
Cons:
- Expensive and unnecessary for general water purification.
- Does not remove contaminants; only changes the pH.
- Scientific basis for health claims is not well established.
How They Work: Under-sink water purifiers are compact devices installed under the kitchen sink that filter water directly from the tap.
Pros:
- Installed under the sink, saving countertop space.
- Multi-stage filtration system removes a wide range of water pollutants.
- Can quickly provide a sufficient amount of clean water.
Cons:
- Some models may require professional installation.
- Filter cartridges need regular replacement.
- Reverse osmosis models produce a certain percentage of wastewater.
Choosing the right water filter depends on various factors, including the quality of your water source, the specific contaminants you want to remove, and your budget. Here are some tips to help you choose:
- Test Your Water: Before choosing a filter, test your water to see what types of contaminants are present.
- Consider Your Needs: Decide if you need a drinking water filter, a whole-house filter, or a portable filter.
- Match the Filter Type to the Contaminants: Choose a filter that targets the contaminants in your water. For example, use an RO filter to remove heavy metals or an activated carbon filter to remove chlorine.
- Evaluate Maintenance Requirements: Some filters require frequent replacement or cleaning, so consider how much maintenance you're willing to perform.
- Budget Considerations: Filters vary widely in price, from inexpensive water filter pitchers to expensive RO systems. Balance your budget with the level of filtration you need.
Understanding the differences between various water purifier filters is crucial for ensuring access to clean and safe drinking water. Each filter type has its unique advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to choose the one that best suits your specific needs and water quality conditions. Whether you opt for a reverse osmosis system, an activated carbon filter, or a UV water purifier, the key is to make an informed decision that prioritizes the health and safety of your household.
For more information on water purification systems and to explore the best options for your home, visit reputable sources and consult with water quality experts. Ensuring clean drinking water is not just about choosing the right filter; it's about investing in the health and well-being of your family.
Pre :
Next :











 Cold Chain Rice Production Line
Cold Chain Rice Production Line Unmanned Intelligent Rice Production Line
Unmanned Intelligent Rice Production Line Automatic Rice Production Line
Automatic Rice Production Line
Ready to Get Started?