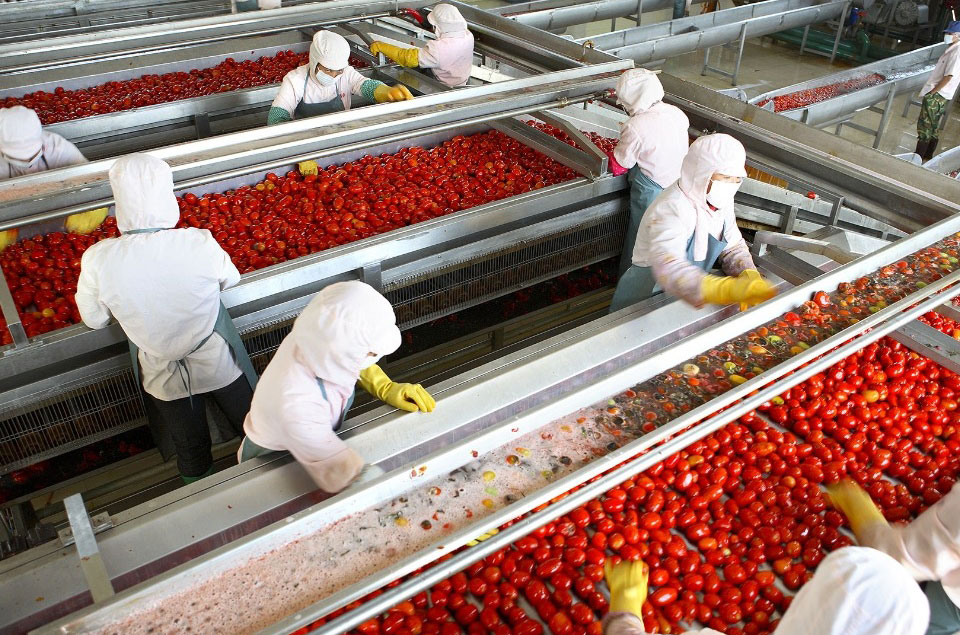

Tomato paste is a staple ingredient in many kitchens worldwide, known for its rich flavor and versatility in various dishes. However, the journey from fresh tomatoes to the concentrated paste involves a meticulous process, with sterilization playing a crucial role. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the sterilization process in tomato paste production lines, exploring its importance, methods, and technological advancements. By the end, you will have a thorough understanding of how this essential step ensures the safety and quality of tomato paste.
Sterilization is a critical step in the production of tomato paste, aimed at eliminating harmful microorganisms that can spoil the product or pose health risks to consumers. The process ensures that the tomato paste remains safe for consumption over an extended period, maintaining its nutritional value and flavor. Without proper sterilization, the paste could harbor bacteria, yeasts, and molds, leading to spoilage and potential foodborne illnesses.
Several methods are employed to sterilize tomato paste, each with its advantages and specific applications. The choice of method depends on factors such as the desired shelf life, production scale, and equipment availability. Here are the most common sterilization techniques used in tomato paste production lines:
Thermal sterilization is the most widely used method in tomato paste production. It involves heating the product to a specific temperature for a set period to kill microorganisms. This method can be further categorized into:
Pasteurization involves heating the tomato paste to a temperature of 70-90°C for a short duration. This process effectively destroys most pathogenic bacteria and extends the product's shelf life. However, it may not eliminate all spores, so pasteurized tomato paste often requires refrigeration.
Sterilization, also known as canning, involves heating the tomato paste to a temperature above 100°C for a longer duration. This method ensures the destruction of all microorganisms, including spores, providing a shelf-stable product that can be stored at room temperature. The process typically involves the use of retort machines or autoclaves.
Aseptic processing is a modern sterilization technique that combines thermal sterilization with sterile packaging. In this method, the tomato paste is heated to a high temperature for a short time and then rapidly cooled. The sterilized paste is then filled into pre-sterilized containers in a sterile environment. Aseptic processing offers several advantages, including longer shelf life, better retention of nutrients and flavor, and reduced energy consumption.
High-pressure processing is a non-thermal sterilization method that uses high pressure to inactivate microorganisms. The tomato paste is subjected to pressures of up to 600 MPa, which disrupts the cellular structure of bacteria, yeasts, and molds. HPP preserves the nutritional quality and sensory attributes of the tomato paste, making it an attractive option for premium products.
UV irradiation is another non-thermal sterilization method that uses ultraviolet light to kill microorganisms. The tomato paste is exposed to UV light, which damages the DNA of bacteria and other pathogens, rendering them inactive. This method is often used as an additional step to enhance the safety of tomato paste, especially in combination with other sterilization techniques.
The field of food processing has seen significant technological advancements in recent years, and sterilization methods for tomato paste production are no exception. Innovations in equipment design, automation, and process control have improved the efficiency and effectiveness of sterilization processes. Here are some notable advancements:
Continuous sterilization systems have revolutionized the tomato paste production industry by providing a more efficient and consistent sterilization process. These systems use a continuous flow of tomato paste through heat exchangers, where it is rapidly heated and cooled. Continuous sterilization reduces processing time, energy consumption, and the risk of contamination.
Modern retort machines are equipped with advanced features such as precise temperature and pressure control, automated monitoring, and data logging. These enhancements ensure uniform sterilization, minimize product degradation, and enhance overall productivity. Some retort systems also incorporate agitation mechanisms to improve heat transfer and reduce processing time.
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) in sterilization processes has brought about significant improvements in efficiency and quality control. IoT-enabled sensors and devices provide real-time data on temperature, pressure, and other critical parameters, allowing for precise monitoring and control. AI algorithms analyze this data to optimize the sterilization process, predict maintenance needs, and ensure consistent product quality.
To achieve optimal results in the sterilization of tomato paste, it is essential to follow best practices and adhere to industry standards. Here are some key considerations:
The quality of the tomatoes used in production directly impacts the effectiveness of the sterilization process. It is crucial to source fresh, ripe tomatoes and ensure proper sorting, washing, and handling to minimize contamination.
Regular maintenance and calibration of sterilization equipment are vital to ensure consistent performance. Routine inspections, cleaning, and servicing help prevent equipment malfunctions and ensure accurate control of temperature and pressure.
Validating the sterilization process is essential to confirm its effectiveness in eliminating microorganisms. This involves conducting microbiological tests, such as spore challenge tests, to verify that the chosen sterilization method achieves the desired level of microbial reduction.
Continuous monitoring of critical parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and processing time, is crucial to ensure the success of the sterilization process. Detailed documentation of these parameters, along with regular audits, helps maintain compliance with regulatory requirements and ensures traceability.
Proper training and education of personnel involved in the sterilization process are essential to ensure adherence to best practices and protocols. Regular training sessions, workshops, and certifications help enhance the knowledge and skills of operators, leading to improved process control and product quality.
The sterilization process in tomato paste production lines is a vital step that ensures the safety, quality, and shelf life of the final product. By employing various sterilization methods, leveraging technological advancements, and following best practices, manufacturers can produce high-quality tomato paste that meets consumer expectations and regulatory standards. As the demand for safe and nutritious food continues to grow, the importance of effective sterilization in food processing cannot be overstated.
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of the sterilization process and staying abreast of industry advancements is crucial for anyone involved in tomato paste production. By prioritizing quality and safety, manufacturers can deliver a product that not only satisfies consumers but also contributes to the overall health and well-being of society.
Pre :
Next :
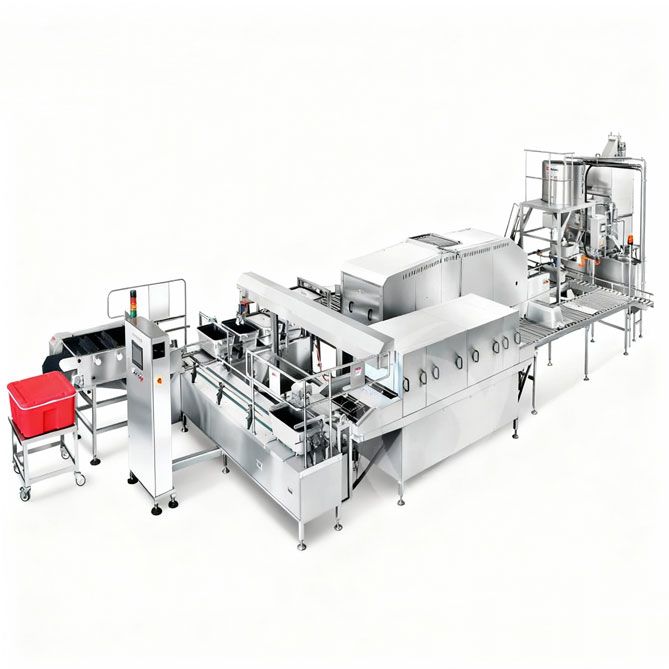
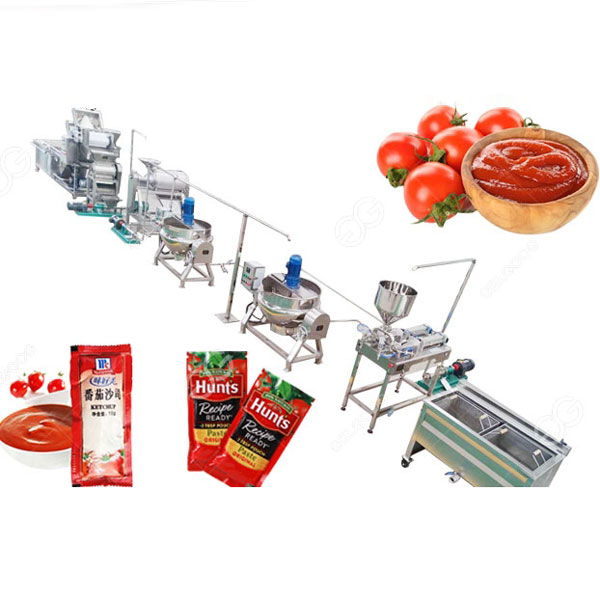










 Small Scale Tomato Sauce Making Machine
Small Scale Tomato Sauce Making Machine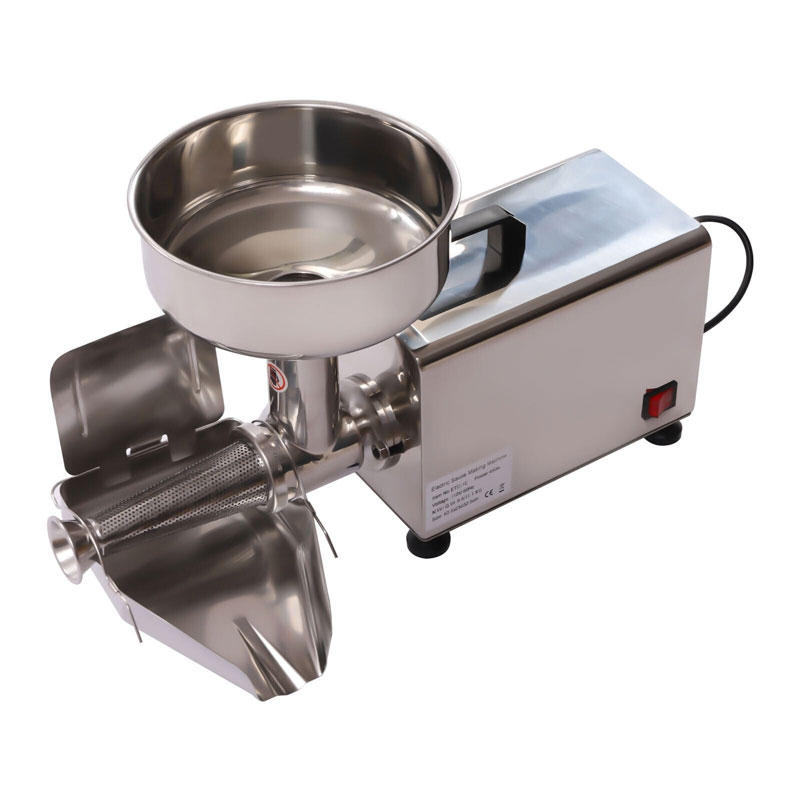 Tomato Sauce Milling Machine
Tomato Sauce Milling Machine Tomato Sauce Grinding Machine
Tomato Sauce Grinding Machine Tomato Juice Processing Production Line
Tomato Juice Processing Production Line
Ready to Get Started?