From Raw Materials to Final Products: A Breakdown of 6 Essential Modules in a High-Efficiency Food Production Line
In today’s fast-evolving food manufacturing industry, building an efficient, automated, and scalable production line is critical to staying competitive. For technical managers, plant engineers, and project planners, understanding the key modules that make up an end-to-end food production line is the foundation for designing a solution that balances productivity, food safety, and flexibility.
This article walks you through the six critical modules of a high-performance food processing line—from raw material intake to final palletizing. We'll explore how system integration, automation, and thoughtful engineering transform each phase into a value-generating segment.
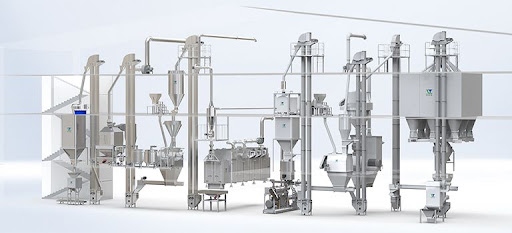
1. Raw Material Conveying: Laying the Foundation for Throughput
Purpose: Efficiently transport bulk raw materials from intake points to the processing area.
Automation Advantages: Our modular conveyors—belt, screw, or pneumatic—are designed to reduce manual handling and contamination risk.
Design Highlights: All contact surfaces are made from food-grade stainless steel, ensuring hygiene compliance.
Why It Matters: A stable, automated conveying system sets the pace for the entire line. Inconsistent or manual feeding often leads to bottlenecks downstream.
2. Cleaning and Sorting: Ensuring Raw Material Quality
Purpose: Remove contaminants and separate substandard materials before processing.
Key Equipment: Bubble washers, rotary drum washers, vibrating sorters, and air classifiers.
Unique Value: Our cleaning units integrate water-saving recirculation systems and automatic discharge for foreign objects.
Impact on Output: Clean and uniformly sorted ingredients drastically improve product quality and minimize wear on downstream equipment.
3. Processing: The Core of Product Transformation
Purpose: Carry out cutting, peeling, mixing, cooking, or other core processing steps.
Flexibility Built-In: We offer customizable modules tailored to specific processes—whether it’s slicing vegetables, emulsifying sauces, or vacuum cooking meat.
Efficiency Gains: Automated controls (temperature, speed, pressure) ensure consistent output while reducing waste and labor.
Food Safety Compliance: Designs follow HACCP and GMP guidelines, with optional CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems.
4. Filling and Packaging: Preserving Freshness and Precision
Purpose: Accurately portion products and seal them in appropriate packaging.
Integrated Systems: Our lines support a wide range of packaging types—pouches, bottles, jars, trays—with quick-change tooling for fast product or size switching.
High-Precision Filling: Servo-driven volumetric fillers, weight-based systems, and anti-drip nozzles ensure accuracy and hygiene.
Why It Matters: Packaging is not just a visual touchpoint—it also affects shelf life, safety, and distribution efficiency.
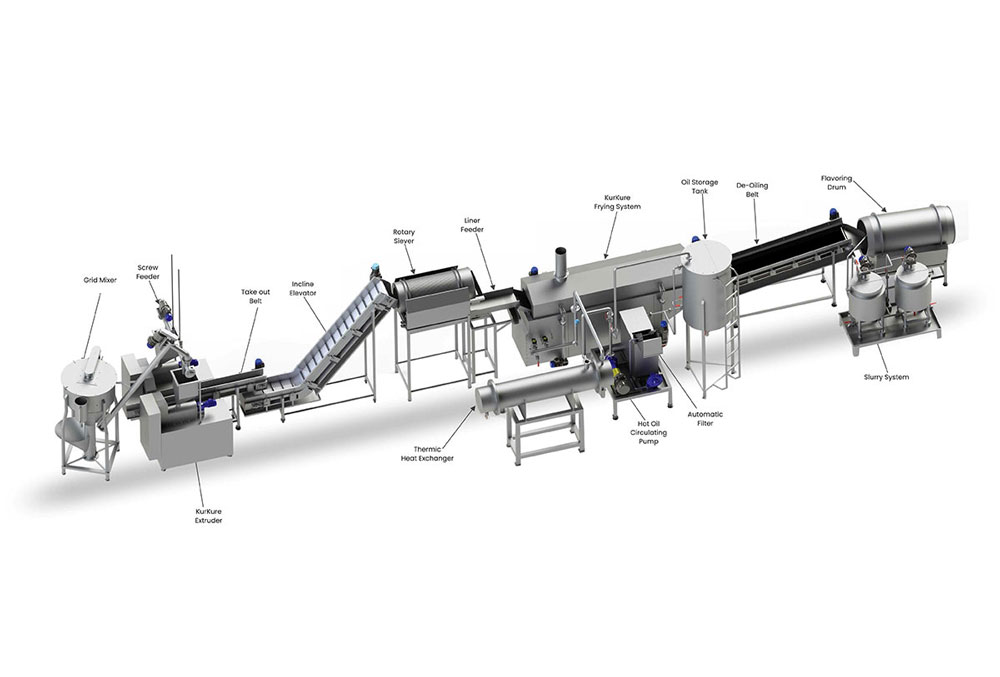
5. Sterilization and Cooling: Protecting Shelf Life and Safety
Purpose: Extend product shelf life while ensuring compliance with food safety regulations.
Technology Options: From continuous pasteurizers and retort sterilizers to flash cooling tunnels and spiral freezers.
Design Advantages: Energy-efficient heat exchangers and real-time temperature monitoring safeguard both food integrity and operating costs.
System Insight: Modular design allows inline integration with minimal footprint, ideal for SMEs or plants with space constraints.
6. Palletizing and End-of-Line Handling: Streamlining Final Logistics
Purpose: Automate the stacking and dispatch preparation of finished goods.
Smart Robotics: Robotic palletizers with vision-guided placement and adaptive stacking algorithms.
Logistics Integration: Optional conveyor-to-truck systems, barcode scanning, and WMS connectivity for smart warehousing.
Why It’s Crucial: A robust end-of-line system ensures fast dispatch, minimizes labor, and reduces packaging damage.
The Importance of Seamless System Integration
A common pitfall in factory design is the use of mismatched or "patchwork" equipment from multiple vendors. This often leads to data silos, mechanical misalignment, and inefficient transitions between processing stages.
Our fully integrated solutions avoid these issues by:
Ensuring end-to-end synchronization
Simplifying maintenance and operator training
Maximizing overall line OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness)
Whether you’re planning a greenfield facility or upgrading an existing one, integrated design ensures all modules “speak the same language”—mechanically, digitally, and operationally.
Conclusion: Build Smarter, Not Just Bigger
In the age of high-mix, high-speed production, a food processing line is only as strong as its weakest link. By understanding and optimizing each of these six core modules—and ensuring they function as a cohesive system—technical leaders can deliver projects that are scalable, safe, and future-ready.
If you're considering building or upgrading a production line, our engineering team offers tailored solutions based on your process, layout, and business goals.
Must-Read Blogs For Chain Restaurants Owner
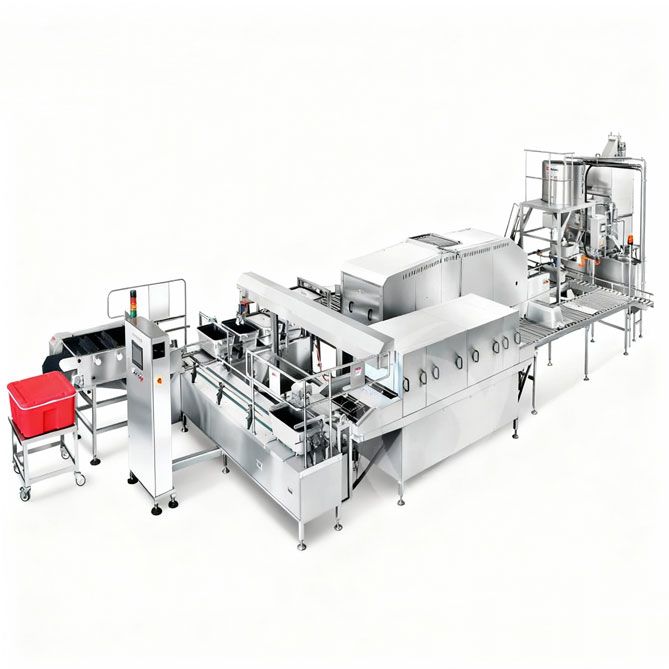










 Cold Chain Rice Production Line
Cold Chain Rice Production Line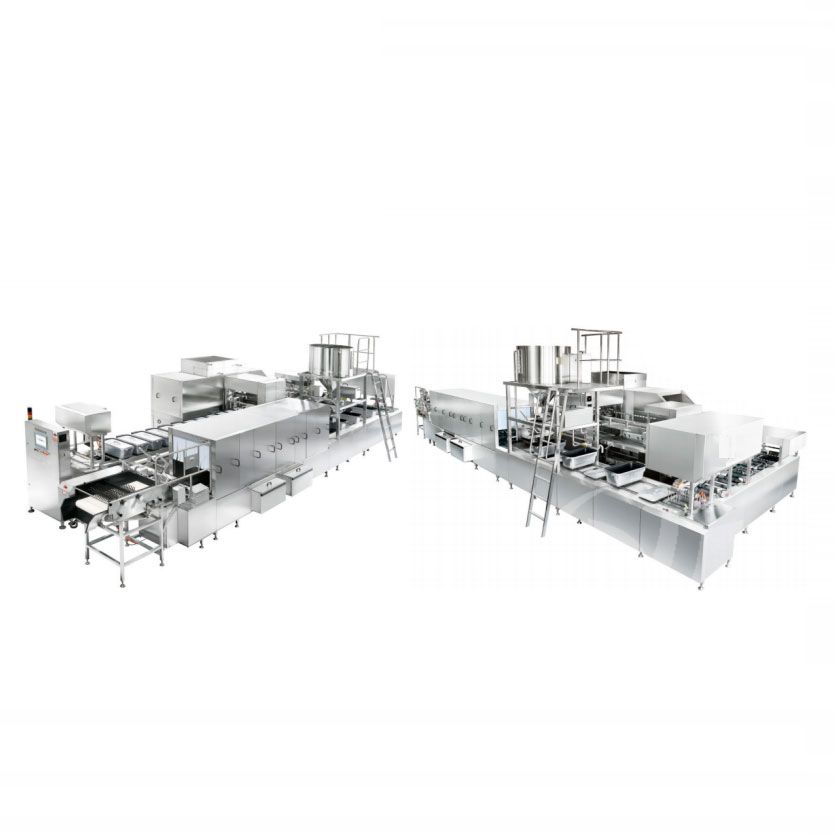 Unmanned Intelligent Rice Production Line
Unmanned Intelligent Rice Production Line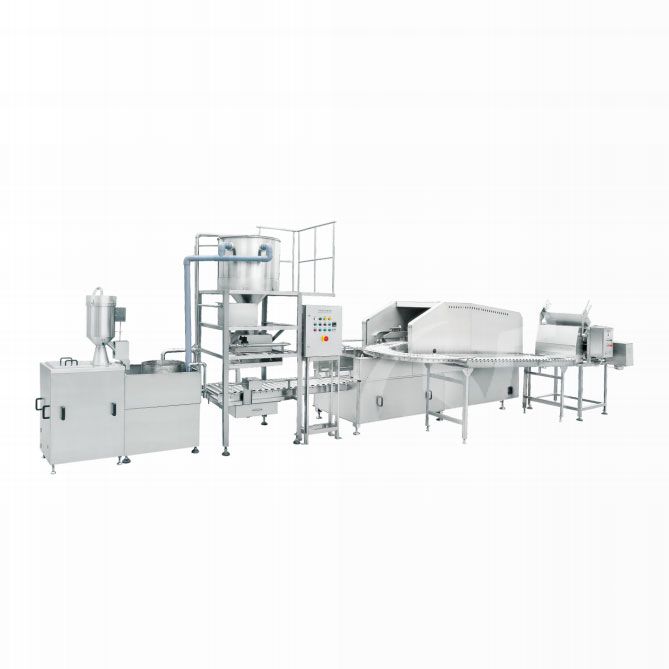 Automatic Rice Production Line
Automatic Rice Production Line
Ready to Get Started?