How to Choose Fish Canning Line Equipment for Southeast Asia
Fish canning is one of the fastest-growing sectors in the Southeast Asian food processing industry. Countries like Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia, and the Philippines are not only major exporters of canned fish but also home to a vibrant domestic market. Choosing the right fish canning line equipment is critical to ensure product quality, operational efficiency, and compliance with international food safety standards.
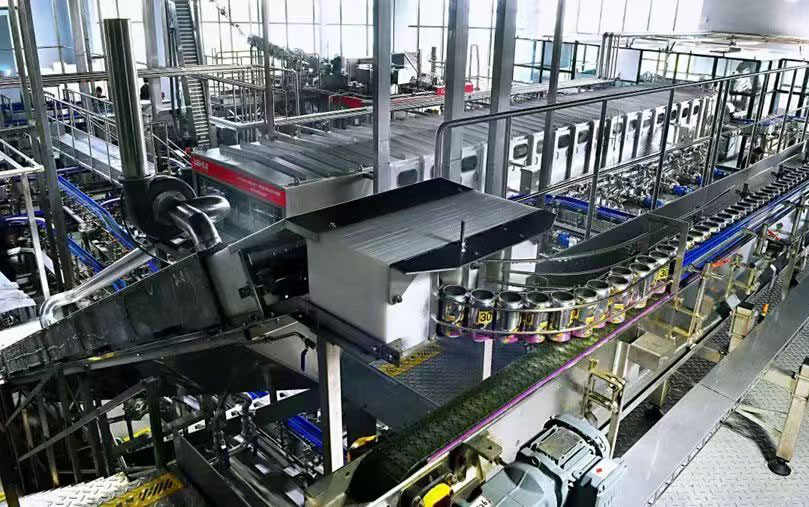

This guide provides a detailed roadmap for food processing businesses to select the most suitable equipment for fish canning, covering market considerations, production capacity, key machinery, quality control, cost analysis, maintenance, and common FAQs.
1. Understanding the Southeast Asian Fish Canning Market
Southeast Asia’s fish canning industry is characterized by high production volume, diverse product types, and a strong export orientation.
Key insights:
Popular Fish Species: Sardines, tuna, mackerel, anchovies, and other small pelagic fish.
Consumer Preferences: Products are often canned in oil, tomato sauce, or brine, with sweet or savory flavor profiles depending on the local market.
Packaging Trends: Easy-open cans dominate, but regular tin cans are also widely used.
Export Requirements: Many producers target EU, US, and Middle East markets, requiring adherence to HACCP, FDA, and EU food safety standards.
Implication for Equipment Selection: Machines must handle various fish types and sauces, accommodate different can sizes, and meet international hygiene and safety standards.
2. Determining Production Scale and Capacity
Choosing the right fish canning line begins with understanding your production requirements:
Small-Scale Operations: Daily output of a few hundred to a few thousand cans. Semi-automatic or single-line equipment is sufficient.
Medium-Scale Factories: Daily output of several thousand to tens of thousands of cans. Requires semi-automatic to fully automated lines with moderate flexibility.
Large-Scale Factories: Daily output of over 100,000 cans. Fully automated multi-line systems are preferred for high efficiency, reduced labor, and consistent quality.
Tip: Match the production line capacity to current and projected demand to avoid underutilization or over-investment.
3. Key Machinery in a Fish Canning Line
A typical fish canning line consists of several essential machines, each critical to product quality and production efficiency.
3.1 Raw Material Preprocessing
Equipment: Fish washers, descalers, evisceration machines, and filleting machines.
Purpose: Clean and prepare fish while minimizing handling damage.
Consideration: Materials should be stainless steel (SUS304) to resist corrosion from saltwater.
3.2 Portioning and Cutting
Equipment: Automatic cutting machines, slicing machines, or portioning conveyors.
Purpose: Ensure uniform fish pieces for consistent filling and thermal treatment.
3.3 Can Filling
Equipment: Liquid and solid filling machines or combination fillers.
Functionality: Accurately fill fish and sauce/oil into cans.
Tip: Precision ±2–3% reduces product waste and maintains consistent weight.
3.4 Seaming / Lid Sealing
Equipment: Double or triple seamers, compatible with easy-open lids if needed.
Purpose: Guarantee airtight sealing to prevent contamination and extend shelf life.
3.5 Sterilization / Retort
Equipment: Batch or continuous steam retorts, water bath sterilizers.
Purpose: Destroy harmful microorganisms and ensure product safety.
Tip: Adjustable temperature and pressure are essential for different fish species and sauces.
3.6 Cooling and Drying
Equipment: Cooling conveyors or water sprays.
Purpose: Prevent can deformation, maintain integrity for labeling and packaging.
3.7 Labeling and Packaging
Equipment: Automatic labeling machines, carton packers, shrink-wrapping machines.
Purpose: Ensure compliance with branding and traceability requirements.
4. Automation and Flexibility Considerations
Semi-Automatic Lines: Suitable for small factories or varied product batches. Lower investment but higher labor requirement.
Fully Automated Lines: Reduce labor, improve consistency, ideal for export-oriented production.
Modular Design: Allows easy scaling and adaptation to different fish species, can sizes, and sauce types.
Tip: In Southeast Asia, labor is affordable, but for export-quality standards, fully automated or modular systems are increasingly preferred.
5. Energy Efficiency and Environmental Considerations
Sterilization, heating, and cooling consume significant energy.
Choose equipment with:
Multi-effect steam recycling
Heat recovery systems
Efficient water usage and waste management
Benefit: Reduces operational costs and environmental footprint, important in regions with rising utility prices.
6. Compliance with Food Safety and Export Standards
HACCP and ISO22000: Ensure traceable, controlled, and hygienic processing.
FDA/EU Certification: Necessary for exports to North America and Europe.
Local Regulations: For example, Thai FDA, Indonesia BPOM, or Philippine FDA standards.
Tip: Ensure the equipment supplier provides certification support and meets hygiene design standards.
7. Maintenance and After-Sales Support
Local Service Availability: Quick repair and spare parts delivery is crucial.
Training: Operator and maintenance training ensure consistent quality and reduce downtime.
Preventive Maintenance: Scheduled inspections for pumps, valves, seaming heads, and sterilizers extend machine lifespan.
8. Cost and ROI Considerations
Equipment Cost:
Small line: $50,000–$150,000
Medium line: $150,000–$500,000
Large automated line: $500,000–$2,000,000
Operational Costs: Labor, utilities, raw material, maintenance.
ROI:
Small to medium lines: 12–24 months.
Large automated lines: 18–36 months depending on scale and efficiency.
Example: A medium-sized sardine processing factory increases output by 30%, reduces labor cost by 20%, and achieves ROI in 18 months using a semi-automatic canning line.
9. Production Process Overview
Raw Fish Handling – Washing, sorting, and preparation
Portioning & Cutting – Uniform fish pieces
Can Washing – Ensure hygienic empty cans
Filling – Fish plus sauce/oil into cans
Seaming – Airtight sealing
Sterilization – Heat treatment to ensure safety
Cooling & Drying – Prepare for labeling
Labeling & Packaging – Traceable, export-ready finished goods
Storage & Distribution – Controlled conditions to maintain quality
10. FAQ: Choosing Fish Canning Line Equipment
Q1: What fish species can the line process?
A1: Sardines, tuna, mackerel, anchovies, and more; equipment must handle different sizes.
Q2: Is the line suitable for small factories?
A2: Yes, semi-automatic or modular lines are ideal for small-scale operations.
Q3: How much does a fish canning line cost?
A3: $50,000–$2,000,000 depending on scale, automation, and capacity.
Q4: What automation level is recommended?
A4: For export-oriented factories, fully automated or modular systems ensure consistent quality.
Q5: How to maintain equipment?
A5: Daily cleaning, weekly inspection, lubrication, and annual preventive maintenance.
Q6: Does it meet export standards?
A6: Choose suppliers providing HACCP, ISO22000, and FDA/EU compliance support.
11. Conclusion
Choosing the right fish canning line equipment for Southeast Asia requires a comprehensive understanding of market demand, production scale, product variety, energy efficiency, and food safety compliance.
By investing in corrosion-resistant, precise, and flexible machinery, food processing businesses can ensure high-quality fish can products that meet local and international standards. Proper maintenance, operator training, and certified equipment will secure consistent output, reduce operational costs, and maximize ROI.
With Southeast Asia’s growing export market and domestic demand, adopting an efficient fish canning line positions manufacturers for long-term success and competitive advantage.
Must-Read Blogs For Chain Restaurants Owner
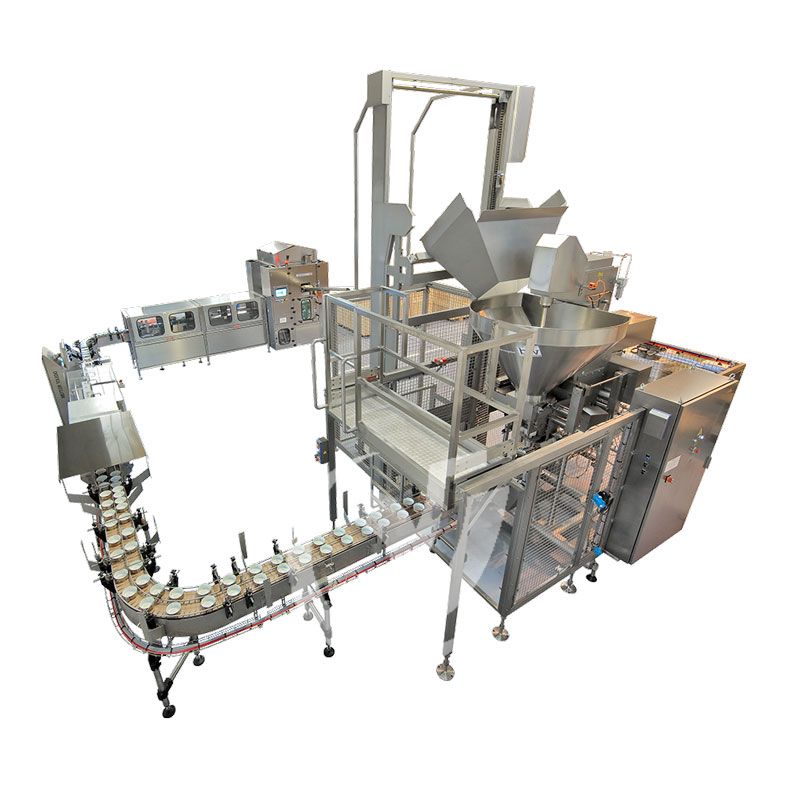
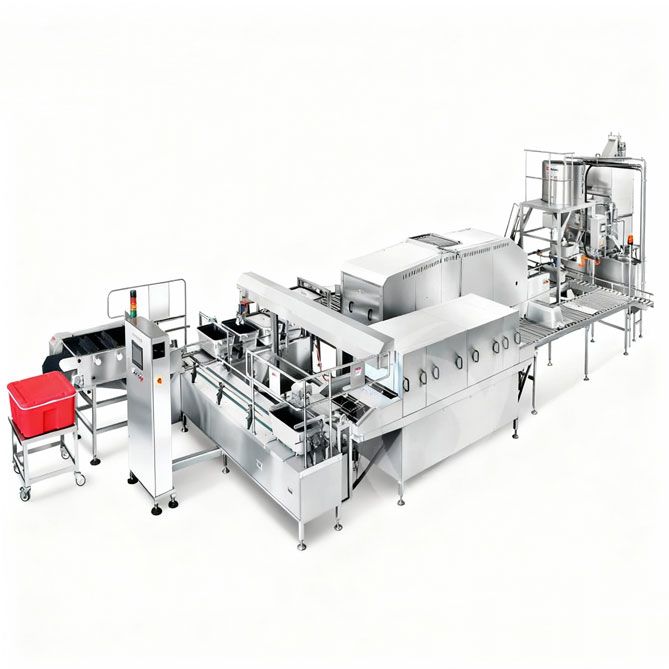










 Eel Canned Food Production Line
Eel Canned Food Production Line
Ready to Get Started?