Production of General Line Cans for Food and Drinks: A Complete Guide for Food Manufacturers
Canned food and beverages are a cornerstone of the global food industry, providing long shelf life, convenience, and safety for consumers. From fruit and vegetable cans to ready-to-drink beverages, the production of canned products requires specialized equipment and streamlined processes. Investing in a general line can production system for food and drinks enables manufacturers to maintain product quality, improve operational efficiency, and maximize profitability.
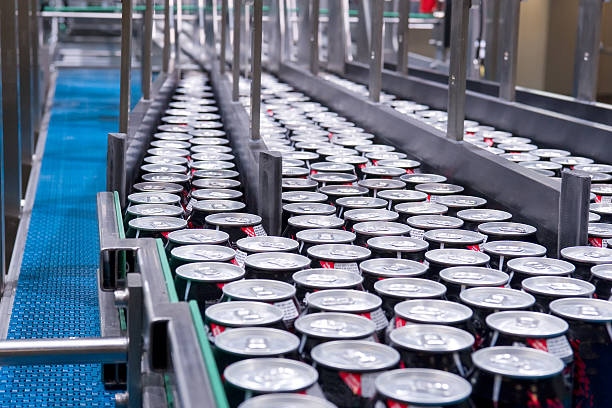

This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the production process, key equipment, quality control measures, cost analysis, and maintenance tips for food and beverage can production lines.
What Is a General Line Can Production for Food and Drinks?
A general line can production system is designed to handle a wide range of products, including solid, semi-solid, and liquid foods, as well as beverages. These production lines integrate multiple stages—from can preparation and filling to sealing, sterilization, and packaging—into an automated or semi-automated workflow.
Key objectives of a general can production line include:
Ensuring product safety and hygiene
Maintaining consistent quality and taste
Improving production efficiency
Reducing operational costs
Supporting a variety of canned products
The flexibility of a general production line makes it suitable for manufacturers of canned fruits, vegetables, meats, fish, sauces, juices, and carbonated or functional drinks.
Key Equipment in a Food and Beverage Can Production Line
A successful can production line relies on several critical machines, each serving a specific purpose in the workflow:
Can Washer
Removes dust, dirt, and contaminants from empty cans before filling.
Stainless steel construction ensures hygiene and durability.
Filling Machine
Handles liquids, semi-liquids, or solid products.
Can be gravity-based, piston-type, or volumetric for precise portioning.
Fully automated models reduce labor and improve efficiency.
Seaming Machine
Seals cans securely to prevent leakage and contamination.
Critical for maintaining product shelf life and meeting food safety standards.
Sterilizer / Retort
Applies heat to destroy pathogens and extend shelf life.
Can use wet or dry heat methods depending on product type.
Supports batch, semi-continuous, or continuous sterilization modes.
Cooling and Drying System
Reduces product and can temperature post-sterilization.
Prepares cans for labeling and packaging.
Labeling and Packaging Machine
Automatically applies labels and packs cans into cartons or trays.
Some systems integrate date coding, batch number printing, and shrink wrapping.
Optional Equipment
Deaerators for oxygen removal in liquid products
Mixing tanks for pre-processing sauces or beverages
Conveyor systems for seamless integration across stages
Step-by-Step Production Process
Understanding the production workflow helps optimize efficiency and maintain quality:
1. Raw Material Preparation
Inspect, wash, and process raw ingredients (fruits, vegetables, meat, fish, or beverages).
Pre-cooking or blanching may be required for certain products.
2. Can Cleaning
Empty cans are washed and sterilized to remove dust and surface bacteria.
Ensures hygiene and prevents contamination during filling.
3. Filling
Products are filled into cans according to type:
Liquids: volumetric filling
Semi-solids: piston or auger filling
Solids: pre-cooked or diced product loading
Accurate portioning ensures uniformity and reduces wastage.
4. Seaming / Sealing
The can lid is tightly sealed using a double seam to prevent leaks.
Proper sealing is critical for shelf stability and safety.
5. Sterilization / Pasteurization
Heat treatment eliminates harmful microorganisms.
Temperature and duration depend on product type and acidity level.
6. Cooling and Drying
Sterilized cans are cooled to safe handling temperatures.
Drying prevents moisture-related label adhesion issues.
7. Labeling and Packaging
Cans are labeled, batch-coded, and packaged into cartons for storage or distribution.
8. Storage and Distribution
Finished products are stored under controlled conditions before shipping.
Proper storage ensures quality until reaching the consumer.
Quality Control Measures
Maintaining consistent quality is crucial in canned food and beverage production. Key measures include:
Hygiene Standards: Comply with HACCP, ISO22000, and GMP.
Can Seal Integrity: Regular inspection to prevent leakage and spoilage.
Microbiological Testing: Monitor bacteria, yeast, and mold levels.
Physicochemical Tests: pH, solids content, viscosity, and flavor consistency.
Batch Traceability: Maintain production logs for recall and quality auditing.
Proper quality control ensures consumer safety, regulatory compliance, and brand reputation.
Choosing the Right Production Line
Selecting an appropriate can production line depends on several factors:
Production Capacity: Evaluate current and projected output requirements.
Product Type: Liquids, semi-solids, and solids require different filling technologies.
Automation Level: Fully automated lines reduce labor and improve throughput; semi-automatic systems suit smaller operations.
Energy Efficiency: Modern equipment optimizes electricity and steam consumption.
Factory Space: Ensure adequate space for equipment, conveyors, and storage.
Supplier Support: Consider warranty, technical support, and spare part availability.
SEO Long-Tail Keywords:
automatic canning machine for food and drinks
food and beverage can production line for medium factories
high-efficiency canning equipment
Cost and ROI Considerations
Equipment Costs
Small-scale lines: $50,000–$150,000
Medium-scale lines: $150,000–$500,000
Large-scale automated lines: $500,000–$2,000,000
Operational Costs
Raw materials and ingredients
Utilities: water, electricity, and steam
Labor
Maintenance and spare parts
ROI Analysis
Small factories typically achieve ROI within 1–2 years.
Automated lines reduce labor and energy costs, improving long-term profitability.
Efficient production reduces raw material waste and enhances product consistency.
Example Case:
A mid-sized beverage factory using a semi-automatic canning line increases output by 30%, reduces labor cost by 20%, and achieves ROI in 18 months.
Maintenance and Operational Tips
Daily Cleaning: Sanitize filling nozzles, conveyors, and can surfaces.
Regular Inspection: Check seaming heads, pumps, and valves.
Lubrication: Maintain moving parts to prevent wear.
Operator Training: Ensure staff follow SOPs and safety protocols.
Preventive Maintenance: Schedule annual servicing to minimize downtime.
Regular maintenance ensures product quality, reduces unplanned stoppages, and extends equipment life.
Market Applications and Trends
Popular Products: Fruit and vegetable cans, meat and fish cans, sauces, juices, and carbonated beverages.
Consumer Trends: Convenience, healthy and natural ingredients, ready-to-eat meals.
Industry Trends: Increasing automation, smart monitoring, energy-efficient machinery, and integration with ERP systems.
Growth Opportunities: Small and medium enterprises can expand by introducing premium or specialty canned products.
FAQ: Production of General Line Cans for Food and Drinks
Q1: What types of products can a general can production line process?
A1: Solid, semi-solid, and liquid foods, as well as beverages.
Q2: What is the typical production capacity?
A2: Small lines: 1,000–5,000 cans/hour; medium lines: 5,000–20,000 cans/hour; large automated lines: up to 100,000 cans/hour.
Q3: How much does a production line cost?
A3: Depending on scale and automation: $50,000–$2,000,000.
Q4: How is product safety ensured?
A4: Through HACCP-compliant procedures, sterilization, quality inspections, and batch traceability.
Q5: Is a semi-automatic line suitable for startups?
A5: Yes, it reduces initial investment while allowing efficient production and scalability.
Q6: How often should equipment be maintained?
A6: Daily cleaning, weekly inspections, and annual preventive maintenance.
Q7: Can the line handle multiple products?
A7: Yes, with adjustable filling, seaming, and sterilization settings, the line can process different types of foods and drinks.
Conclusion
A general line can production system for food and drinks is an essential investment for modern food and beverage manufacturers. By integrating high-quality filling, seaming, sterilization, and packaging equipment, manufacturers can produce safe, consistent, and profitable canned products.
Selecting the right equipment, maintaining strict quality control, optimizing production efficiency, and ensuring proper maintenance are critical for achieving long-term ROI. With increasing consumer demand for convenient, healthy, and ready-to-eat products, an efficient canning production line positions businesses to capitalize on market growth and industry trends.
Must-Read Blogs For Chain Restaurants Owner










 Cold Chain Rice Production Line
Cold Chain Rice Production Line Unmanned Intelligent Rice Production Line
Unmanned Intelligent Rice Production Line Automatic Rice Production Line
Automatic Rice Production Line
Ready to Get Started?