Special Requirements for Fish Canning Line Equipment and Environment in Southeast Asia
The fish canning industry is a cornerstone of the Southeast Asian food processing sector. Countries such as Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia, and the Philippines have become global hubs for fish canning, supplying both domestic and international markets. While standard fish canning equipment works in many regions, operating in Southeast Asia comes with unique environmental and operational challenges. Selecting the right equipment and designing an appropriate production environment is critical to ensure product quality, safety, and efficiency.
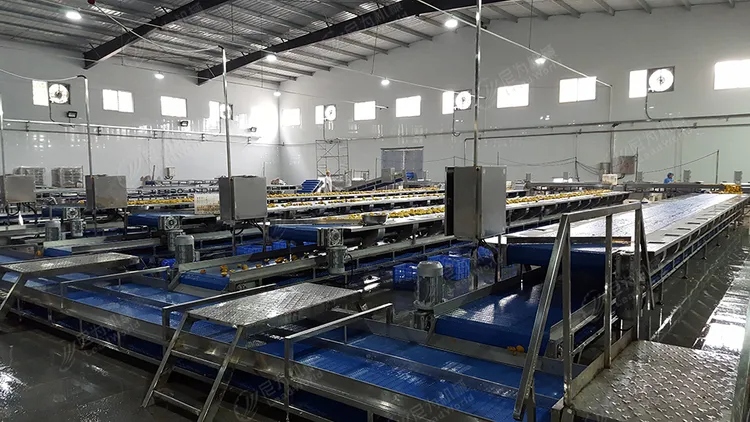

This comprehensive guide explores the special requirements for fish canning line equipment and production environment in Southeast Asia, offering insights into equipment selection, environmental adaptations, quality control, cost considerations, and operational best practices.
1. Understanding the Southeast Asian Fish Canning Market
Southeast Asia is one of the largest producers and exporters of canned fish products in the world.
Key market insights:
Popular Fish Types: Sardines, tuna, mackerel, anchovies, and small pelagic fish.
Consumer Preferences: Cans often contain oil, tomato sauce, soy sauce, or brine. Taste profiles vary regionally—some markets prefer sweet flavors, others savory.
Packaging Trends: Easy-open cans dominate, though traditional tin cans remain in use.
Export Standards: Many factories export to Europe, the United States, and Japan, requiring compliance with HACCP, ISO22000, FDA, and EU regulations.
Implication for Equipment: Machines must accommodate multiple fish types, sauces, and can sizes, while maintaining hygienic standards for export.
2. Special Equipment Requirements
Operating in Southeast Asia presents unique challenges due to climate, raw material characteristics, and high production demands.
2.1 Corrosion Resistance
Coastal sourcing of fish exposes equipment to saltwater.
Equipment must be made from SUS304 stainless steel or higher, including pumps, valves, conveyors, and processing tanks.
Internal linings and critical components must resist corrosion and maintain hygiene.
2.2 High Temperature and Humidity Adaptation
Tropical climate: high heat and humidity can affect machinery and electronics.
Electrical systems, PLCs, sensors, and control panels require IP65+ protection.
Components should withstand continuous operation in humid conditions without failure.
2.3 Automation and High Production Efficiency
Southeast Asian factories often process high volumes for export.
Fully automated lines are preferred for:
Consistent quality
Reduced labor dependency
Continuous production
Semi-automatic or modular lines may suit smaller factories or varied product types.
2.4 Flexibility for Multiple Fish Species and Sauces
Equipment must handle sardines, mackerel, tuna, anchovies, etc.
Filling machines must accommodate oil, tomato sauce, brine, and soy sauce.
2.5 Energy Efficiency and Resource Conservation
Sterilization, heating, and cooling consume significant energy.
Select equipment with multi-effect steam recovery, heat recycling, and water-saving designs to reduce operational costs.
3. Production Environment Requirements
3.1 Temperature and Humidity Control
Production areas must have ventilation and air conditioning to maintain stable temperature and humidity.
Proper environmental control prevents fish spoilage and microbial growth.
Critical zones: filling, sealing, and post-sterilization cooling.
3.2 Hygiene and Sanitation
Compliance with HACCP and ISO22000 is essential.
Factory layout should include zoned areas: raw material handling, filling, sterilization, packaging, and storage to prevent cross-contamination.
Floors, walls, and drains must support easy cleaning and disinfection.
3.3 Pest and Contamination Control
Tropical climates have higher risks of insects and rodents.
Implement:
Sealed storage areas
Door curtains and airlocks
Pest control measures and proper waste management
Filling and packaging areas may require positive air pressure or filtered air.
3.4 Post-Sterilization Cooling and Storage
Rapid cooling prevents can deformation and maintains quality.
Storage areas must be dry and temperature-controlled before labeling and packaging.
3.5 Reliable Energy and Water Supply
Steam boilers, hot water, and compressed air systems require stable supply.
Water must meet food-grade quality standards, particularly for sauces and brines.
4. Key Equipment Components in Southeast Asian Fish Canning Lines
Raw Material Preparation: Washers, descalers, eviscerators, and filleting machines.
Cutting and Portioning: Automatic slicing and portioning machines ensure uniform fish pieces.
Can Washing: Hygienic cleaning before filling.
Filling Machines: Accurate liquid and solid filling compatible with different sauces.
Seaming Machines: Double or triple seamers for airtight sealing; easy-open lid options if required.
Sterilization / Retorts: Batch or continuous sterilizers with adjustable temperature and pressure.
Cooling and Drying Systems: Rapid cooling conveyors to maintain can integrity.
Labeling and Packaging Machines: Automatic labeling, batch coding, and carton packing.
Tip: All equipment should be stainless steel, corrosion-resistant, and compatible with humid tropical conditions.
5. Quality Control Considerations
Hygiene and Safety: HACCP, ISO22000, and GMP compliance.
Seam Integrity: Regular checks to prevent leakage and spoilage.
Microbial Testing: Monitor for bacteria, yeast, and mold.
Physicochemical Tests: pH, solids content, viscosity, and flavor.
Batch Traceability: Essential for exports and product recalls.
6. Maintenance and Operational Tips
Daily Cleaning: Sanitize filling nozzles, conveyors, and contact surfaces.
Weekly Inspections: Check seaming heads, pumps, and valves.
Lubrication: Maintain moving parts to prevent wear and corrosion.
Operator Training: Ensure SOP compliance and safety awareness.
Preventive Maintenance: Annual servicing reduces downtime and prolongs equipment life.
7. Cost and ROI Considerations
Small Lines: $50,000–$150,000; suitable for startups or small-scale operations.
Medium Lines: $150,000–$500,000; semi-automatic or modular systems for export markets.
Large Lines: $500,000–$2,000,000; fully automated high-capacity lines for continuous production.
ROI: Typically ranges 12–36 months, depending on scale, efficiency, and energy savings.
8. Production Workflow Overview
Raw fish handling (washing, sorting, preparation)
Cutting and portioning
Can washing
Filling with fish and sauce/oil
Seaming / lid sealing
Sterilization / retort
Cooling and drying
Labeling and packaging
Storage and distribution
9. FAQ
Q1: Can the line process different fish species?
A1: Yes, with adjustable cutting, filling, and sterilization parameters.
Q2: Is the line suitable for small-scale factories?
A2: Semi-automatic and modular lines are ideal for small operations.
Q3: How is equipment adapted for tropical climates?
A3: Stainless steel construction, IP65 electrical components, and humidity-resistant controls.
Q4: What export certifications are required?
A4: HACCP, ISO22000, FDA, EU standards depending on destination markets.
Q5: How often should maintenance be performed?
A5: Daily cleaning, weekly inspection, and annual preventive maintenance are recommended.
10. Conclusion
Operating a fish canning factory in Southeast Asia requires careful equipment selection and production environment planning. Factors such as high humidity, saltwater corrosion, tropical temperatures, and export quality standards make it essential to choose stainless steel, corrosion-resistant, energy-efficient, and automated equipment.
A well-designed production environment with temperature and humidity control, pest prevention, sanitation zoning, and reliable utilities ensures consistent product quality and compliance with international standards.
By considering these special requirements, food manufacturers can optimize fish canning operations, reduce operational risks, and achieve higher ROI, positioning themselves for success in both domestic and global markets.
Must-Read Blogs For Chain Restaurants Owner









 Dual-Roll Steamed Bun Machine
Dual-Roll Steamed Bun Machine Food X-ray Foreign Object Detector
Food X-ray Foreign Object Detector Commercial Stufed Meatball Forming Machine
Commercial Stufed Meatball Forming Machine
Ready to Get Started?