What Equipment Is Needed For Producing Canned Goods
A Complete Guide for Food Manufacturers, Processors, and Entrepreneurs
The global canned food market continues to expand rapidly, driven by consumer demand for convenient, long-lasting, and ready-to-eat products. Whether you’re planning to produce canned fish, fruits, vegetables, sauces, or ready meals, one crucial question always arises:
👉 What equipment is actually needed to produce canned goods efficiently and safely?
In this complete guide, we’ll explain the core machines, auxiliary systems, and key considerations for setting up a modern canned goods production line. You’ll also learn about production capacity ranges, cost estimates, and how to choose the right canning equipment for your factory.
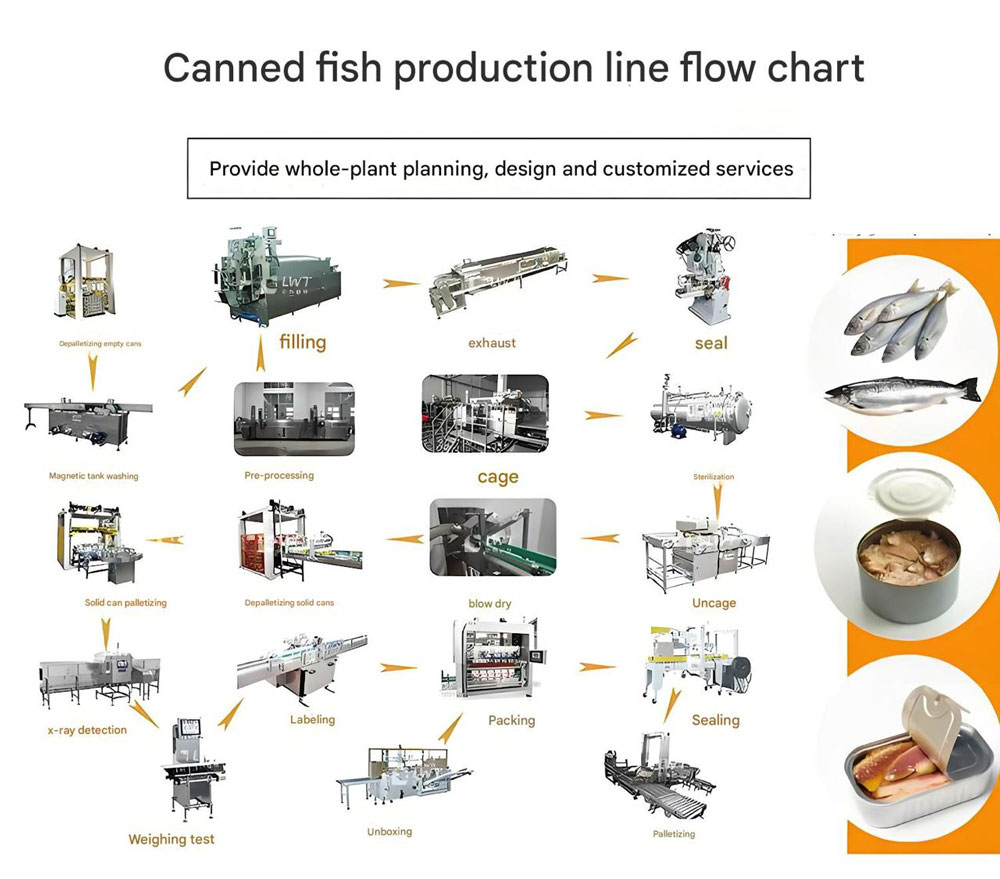
1. Overview: How Canned Food Production Works
Canning is a food preservation process that involves sealing food in airtight containers and sterilizing them through heat treatment to prevent spoilage.
A canned goods production line integrates all stages — from raw material preparation to sealing and labeling — into a continuous, semi-automated, or fully automated system.
Core Production Stages:
Raw Material Preparation
Filling and Sealing
Sterilization
Cooling and Drying
Labeling and Packaging
Each stage requires specialized machines designed for different product types and container materials (tin cans, aluminum cans, or glass jars).
2. Essential Equipment for Producing Canned Goods
Below is a breakdown of the key equipment categories used in canned goods production lines.
2.1 Raw Material Washing and Sorting Machines
Purpose:
To clean, inspect, and classify raw ingredients (fruits, vegetables, meat, or seafood) before processing.
Typical Equipment:
Bubble washing machine – Removes surface dirt, sand, and pesticide residues.
Rotary drum washer – Ideal for root vegetables or large fruit.
Sorting conveyor belt – Operators manually remove defective items.
Inspection tables – For visual quality checks before processing.
Recommended Capacity:
300–2,000 kg/h depending on product type.
2.2 Peeling, Cutting, and Preprocessing Equipment
Before filling, food materials often require peeling, slicing, chopping, or blanching.
Common Machines:
Fruit and vegetable peelers (for mango, pineapple, tomato, carrot, etc.)
Cutting or slicing machines
Meat grinders or fish cutters
Blanching machine – Light heat treatment to preserve color and texture.
Automation Level:
Semi-automatic to fully automatic, depending on production size.
2.3 Cooking and Mixing Equipment
Cooking or preheating softens the raw ingredients and enhances flavor. For sauces, beans, and meats, a mixing or boiling system is used.
Examples:
Steam jacketed kettles – Used for sauces, soups, and pastes.
Automatic stirring pots – Prevent burning and ensure even heating.
Vacuum cookers – Retain flavor and color in fruit preserves.
Temperature Range:
60–120°C, depending on food type and desired outcome.
2.4 Filling Machines
Filling machines accurately dispense product into cans or jars. They are the heart of a canning line and directly impact efficiency and hygiene.
Types of Filling Machines:
Liquid filling machine – For juice, syrup, or sauce.
Paste filling machine – For viscous products like ketchup or condensed milk.
Solid filling machine – For meat chunks, vegetables, or fish.
Vacuum or piston-type filler – Ensures precise quantity and minimal air inside the can.
Key Features to Look For:
Adjustable filling volume
Stainless steel contact surfaces
Compatibility with different can sizes
Integration with conveyor systems
Production Capacity:
1,000–20,000 cans/hour (small to large scale)
2.5 Sealing or Closing Machines
Once filled, cans or jars are sealed to create an airtight environment. Proper sealing prevents bacterial contamination and spoilage.
Main Types:
Can seaming machine (for tin or aluminum cans)
Vacuum sealer (for glass jars)
Twist cap machine (for jarred products)
Key Specifications:
1 to 4 heads depending on output speed
Compatible with both round and irregular cans
Stainless steel construction for hygiene
Automation Level:
Manual → Semi-automatic → Fully automatic
2.6 Sterilization Equipment (Retort Machines)
The sterilizer (retort) is one of the most critical components in canned food production. It ensures food safety by destroying microorganisms and enzymes.
Common Types:
Steam retort (autoclave)
Water spray retort
Rotary retort
Hydrostatic sterilizer
Operating Parameters:
Temperature: 110–135°C
Pressure: 0.2–0.5 MPa
Cycle time: 30–90 minutes
Material:
Full stainless steel with automatic temperature & pressure control.
Output Capacity:
500–10,000 cans per cycle, depending on chamber size.
2.7 Cooling and Drying Systems
After sterilization, cans are cooled to stop further cooking and prevent deformation.
Equipment Options:
Cooling conveyor
Water shower tunnel
Air drying machine
Proper cooling ensures label adhesion and prevents can swelling.
2.8 Labeling, Coding, and Packaging Machines
The final stage involves branding and packaging before distribution.
Key Machines:
Labeling machine – Wrap-around or top/bottom label application.
Inkjet printer – Prints production date, batch number, and expiry.
Carton packing machine – Packs cans into boxes or shrink-wrapped trays.
Palletizer – Stacks boxes for storage and shipping.
3. Auxiliary Systems for Canning Factories
In addition to the core machines, several supporting systems are vital for smooth operation:
3.1 Steam Boiler
Provides heat energy for sterilization and cooking processes.
3.2 Water Treatment System
Ensures clean, mineral-free water for washing and cooking.
3.3 Air Compressor
Powers pneumatic controls, seaming heads, and conveyors.
3.4 Conveyor Systems
Integrate the entire production line, ensuring continuous material flow.
3.5 CIP (Clean-In-Place) System
Automated cleaning of tanks and pipelines to maintain hygiene.
4. Layout of a Standard Canned Goods Production Line
A small or medium-sized canning plant typically follows this layout:
Raw Material → Washing → Cutting → Cooking → Filling → Sealing → Sterilizing → Cooling → Labeling → Packaging → Storage
Efficient layout planning reduces labor, saves space, and enhances production efficiency.
Factories usually require 300–800 m² for a small-scale setup and 1,500–3,000 m² for a medium plant.
5. Cost of Canning Equipment
The total cost varies depending on product type, capacity, and automation level.
| Production Scale | Output (Cans/Hour) | Estimated Cost (USD) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small-Scale Line | 1,000–3,000 | $80,000 – $150,000 | Semi-automatic |
| Medium-Scale Line | 3,000–8,000 | $200,000 – $400,000 | Partial automation |
| Large-Scale Line | 10,000–20,000 | $500,000 – $1,000,000+ | Fully automated |
Additional costs:
Factory construction
Utilities (steam, water, electricity)
Packaging materials
Quality testing equipment
6. How to Choose the Right Canning Equipment Manufacturer
1. Define Your Product Range
Different machines are used for meat, fish, vegetables, or sauces. Choose a manufacturer with experience in your product category.
2. Assess Production Capacity Needs
Plan for at least 30% higher than your initial target to allow for growth.
3. Check Quality Certifications
Look for ISO, CE, or HACCP certifications for global compliance.
4. Evaluate After-Sales Support
Ensure the supplier provides installation, training, and technical support.
5. Consider Turnkey Solutions
Top Chinese suppliers such as Qingdao Hongshengyuanlin Co., Ltd., Zhucheng Zhongyu Machinery, and Shanghai Leadworld Machinery offer complete turnkey canning lines, from design to commissioning.
7. Maintenance and Quality Control Tips
Perform daily sanitation of filling and sealing zones.
Regularly check seam integrity using a can seam analyzer.
Calibrate temperature and pressure sensors in sterilizers.
Maintain accurate product traceability with date coding systems.
8. Future Trends in Canning Technology
Modern canning lines are evolving with:
Smart sensors for real-time process monitoring.
Robotic packaging systems.
Energy-efficient sterilization technologies.
AI-based production control for predictive maintenance.
Automation and sustainability will continue driving innovation, helping processors reduce costs and environmental impact.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the minimum investment for a canned goods production line?
A small-scale semi-automatic canning line can start from $80,000–$100,000, depending on the product type and capacity.
Q2: Can the same line produce different canned foods?
Yes. Many lines are multi-functional, allowing for quick changeovers between products such as vegetables, sauces, or seafood.
Q3: What type of cans can be used?
Tinplate, aluminum, or glass jars — depending on product and market preference.
Q4: How long does it take to install a canning line?
Typically 30–60 days, including assembly, testing, and staff training.
Q5: How long is the shelf life of canned foods?
Properly sterilized canned foods can last 1–3 years, depending on the formulation and storage.
10. Conclusion
Setting up a canned goods production line requires careful planning and the right equipment selection. From washing and filling to sealing and sterilizing, every step must ensure food safety, efficiency, and consistency.
By investing in reliable machinery and working with experienced manufacturers, even small and medium-sized businesses can build profitable canning operations with high output and long-term scalability.
Whether you’re producing canned fish, fruits, or ready meals, a properly designed canning line will help your brand deliver safe, high-quality products that meet both domestic and international standards.
Must-Read Blogs For Chain Restaurants Owner
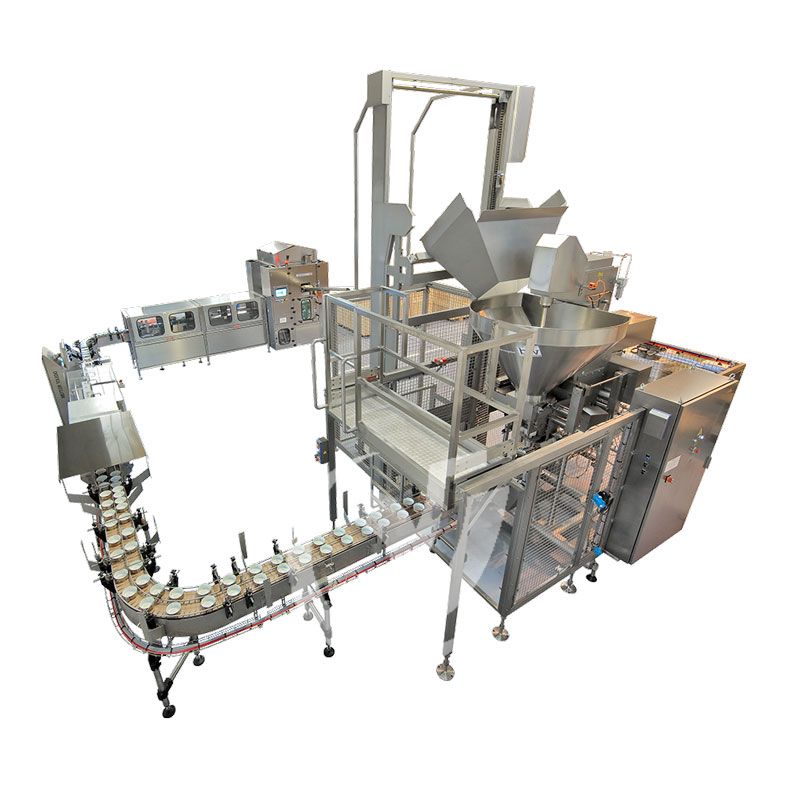
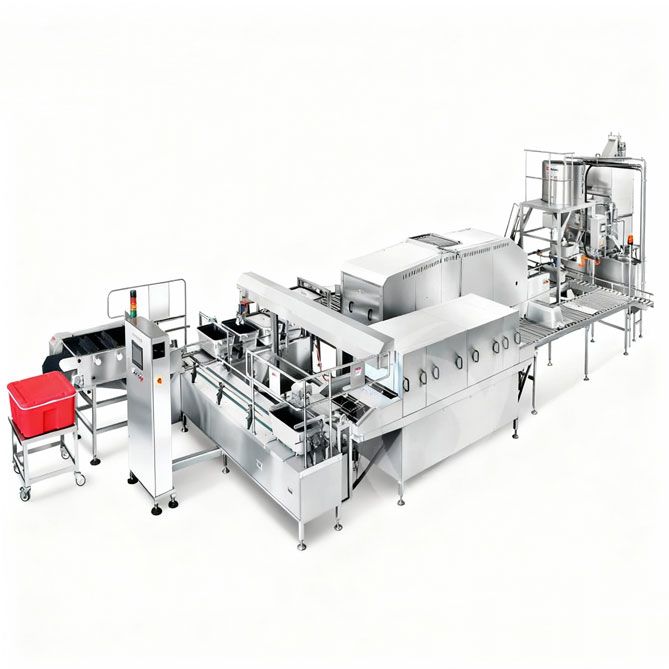










 Aseptic Canning Production Line Equipment
Aseptic Canning Production Line Equipment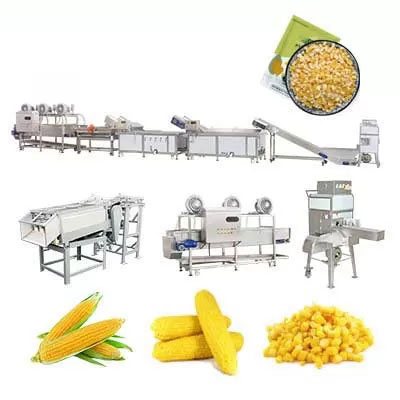 Sweet Corn Canning Production Line
Sweet Corn Canning Production Line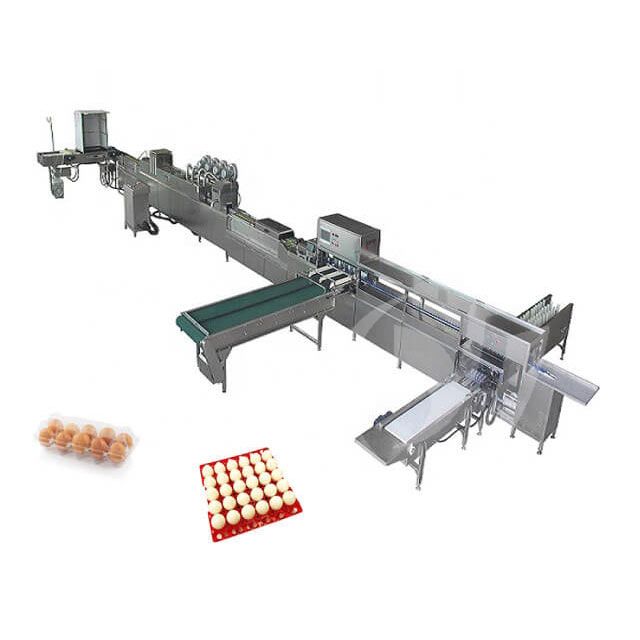 Egg Canning Production Line
Egg Canning Production Line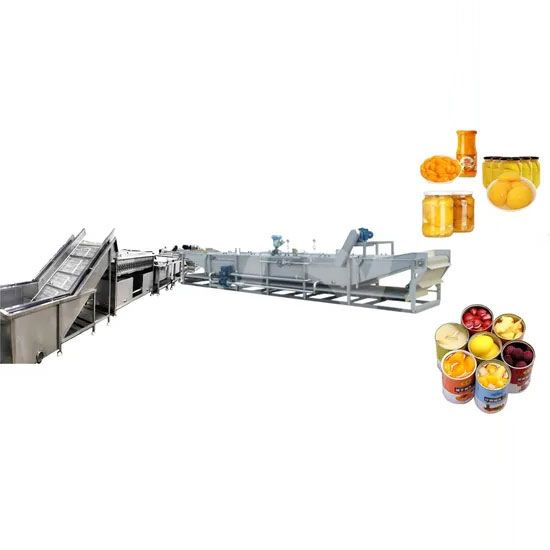 Canned Fruit Production Line Equipment
Canned Fruit Production Line Equipment
Ready to Get Started?