How to Automate Your Mushroom Canning Factory
Automating a mushroom canning factory is no longer a forward-looking concept—it is a practical requirement for producers facing rising labor costs, tighter food safety regulations, and increasing pressure for consistent product quality. How to Automate Your Mushroom Canning Factory is a question now being asked by industrial mushroom processors who must balance throughput, hygiene, yield, and long-term operating cost in a highly competitive global market.
This article is written for factory owners, production managers, process engineers, and procurement teams involved in canned mushroom production. It focuses on real production environments, not theoretical automation. The objective is to explain how automation is implemented across a mushroom canning line, what problems it solves, how equipment choices affect performance, and how to plan capacity and investment with a long-term operational perspective.

What Automation in a Mushroom Canning Factory Means and How It Works
Automation in a mushroom canning factory refers to the systematic replacement of manual, labor-intensive, and variable operations with integrated mechanical, electrical, and control systems that deliver stable output and predictable quality. It is not limited to adding machines; it is about redesigning the process flow to minimize human intervention at critical control points.
A fully or semi-automated mushroom canning factory typically integrates the following stages:
Raw Mushroom Handling and Pre-Processing
Fresh mushrooms are highly sensitive to mechanical damage, enzymatic browning, and microbial growth. Automation begins at raw material reception with controlled unloading, conveying, and sorting systems that reduce manual handling.
Key automated functions include:
Water flume or belt conveying to minimize bruising
Automatic washing and debris removal
Optical or mechanical grading by size and quality
Trimming and slicing systems with adjustable cutting geometry
Automated pre-processing ensures uniform raw material quality, which directly impacts downstream filling accuracy and visual consistency.
Blanching and Color Stabilization
Blanching is a critical step in mushroom canning, used to inactivate enzymes, reduce microbial load, and stabilize color and texture.
Automated blanching systems use:
Controlled time–temperature profiles
Continuous belt or screw blanchers
Automatic water and energy management
Precise blanching automation reduces yield loss from overcooking and prevents discoloration during storage.
Automated Filling and Brining
Filling mushrooms into cans is one of the most challenging steps to automate due to variable piece size and bulk density.
Modern automated filling systems combine:
Volumetric or weight-based solid fillers
Gentle product distribution mechanisms
Brine or liquor dosing with synchronized control
Automation here ensures consistent fill weight, controlled headspace, and reduced product damage—key factors in vacuum stability and finished appearance.
Exhausting, Seaming, and Vacuum Control
In an automated mushroom canning factory, exhausting and seaming are tightly linked through control logic.
Key automated elements include:
Steam flow exhausting tunnels
Inline vacuum monitoring
Multi-head double seamers with recipe management
Automation ensures repeatable seam integrity and minimizes oxygen content, which is critical for shelf life and corrosion prevention.
Retorting and Thermal Processing
Thermal processing is the core food safety step in mushroom canning.
Automated retort systems provide:
Precise temperature and pressure control
Automated loading and unloading
Digital process recording for traceability
Automation at this stage reduces operator error and ensures compliance with process authority requirements.
Post-Retort Handling and Packaging
After sterilization, automated cooling, drying, inspection, labeling, and packing systems protect product integrity and prepare cans for distribution.
These downstream systems are essential for maintaining seam quality and minimizing handling damage.
Industry Problems Automation Solves in Mushroom Canning
Understanding how to automate your mushroom canning factory requires recognizing the production problems automation is designed to eliminate.
Rising Labor Cost and Labor Availability
Mushroom processing is traditionally labor-intensive, especially in trimming, filling, and handling stages. Automation reduces dependence on manual labor and stabilizes production output in regions facing workforce shortages.
Automated systems also reduce ergonomic strain and improve workplace safety.
Yield Loss and Product Damage
Manual handling often leads to:
Broken mushroom pieces
Inconsistent fill weights
Excessive trimming loss
Automation introduces gentle handling and precise dosing, improving usable yield per kilogram of raw mushrooms.
Hygiene Risks and Food Safety Exposure
Mushrooms are high-moisture products with significant microbial risk. Automation reduces human contact at critical points, lowering contamination risk and supporting HACCP compliance.
Closed systems, CIP-capable equipment, and controlled environments are central to automated factory design.
Inconsistent Product Quality
Manual operations result in variability in slice thickness, fill appearance, and vacuum level. Automation standardizes these parameters, ensuring consistent product quality across batches and shifts.
Scalability Constraints
Manual factories struggle to scale without proportional increases in labor. Automated mushroom canning factories are modular, allowing capacity expansion through additional machines or parallel lines.
Key Features and Technical Advantages of Automated Mushroom Canning Lines
From an engineering perspective, automation delivers advantages that go beyond labor reduction.
Integrated Control Systems
Centralized PLC and HMI platforms allow:
Recipe-based changeover
Real-time monitoring of critical parameters
Data logging for quality and traceability
This integration improves decision-making and reduces downtime.
Gentle Product Handling Design
Automated mushroom equipment uses:
Low-drop-height conveyors
Controlled flow chutes
Soft-transfer mechanisms
These designs preserve product structure and appearance.
Precision in Filling and Seaming
Servo-driven fillers and modern seamers deliver high repeatability, reducing rework and rejects.
Energy and Utility Optimization
Automated systems optimize:
Steam usage in blanchers and retorts
Water recirculation in washing systems
Electrical load balancing across the line
This contributes directly to lower operating cost per unit.
Typical Applications and Production Scenarios
Automated mushroom canning factories are commonly used for:
Whole button mushrooms in brine
Sliced mushrooms for foodservice and retail
Mixed vegetable mushroom products
Private-label and export-oriented SKUs
In real production environments, automation is often introduced in phases, starting with filling and seaming, then expanding upstream and downstream as volumes grow.
Capacity Options and Selection Guidance
When planning how to automate your mushroom canning factory, capacity selection should be driven by realistic demand and future expansion plans.
Key considerations include:
Cans per minute required per SKU
Seasonal raw material availability
Changeover frequency between sizes and formats
Available factory space and utilities
Balanced line design is critical. Oversizing fillers without matching retort capacity leads to bottlenecks and underutilized equipment.
Buyer Benefits: Efficiency, Quality, and Long-Term ROI
Automation delivers measurable benefits for mushroom canning operations.
Higher Operational Efficiency
Automated lines achieve higher OEE through stable cycle times and reduced unplanned stoppages.
Labor Reduction and Cost Control
Fewer operators are required per shift, and labor costs become more predictable.
Improved Product Quality
Uniform slicing, filling, and sealing improve appearance, shelf life, and customer acceptance.
Scalable Investment Model
Automation supports phased investment, allowing factories to grow capacity without disrupting existing production.
Customization and Engineering Support
Every mushroom canning factory has unique constraints related to raw material quality, building layout, and market requirements.
Customization may include:
Adjusting cutting systems for local mushroom varieties
Designing fillers for specific piece sizes
Integrating new automation with legacy equipment
Effective automation projects rely on close collaboration between the equipment manufacturer and the factory’s engineering team from layout design through commissioning.
Standards, Certifications, and Compliance
Automated mushroom canning factories are typically designed to meet:
CE machinery safety requirements
HACCP-based food safety systems
ISO 9001 quality management standards
FDA-oriented hygienic design and thermal process validation principles
Automation simplifies compliance by improving process control and documentation.
Conclusion and Professional Perspective
For producers facing labor pressure, quality demands, and growth targets, understanding how to automate your mushroom canning factory is a strategic necessity rather than a technical curiosity. Automation is not about replacing people; it is about stabilizing processes, protecting product value, and creating a production platform that can adapt to future market demands.
Early-stage engineering evaluation, realistic capacity planning, and phased implementation are the most effective ways to ensure that automation investments deliver long-term operational and financial benefits in mushroom canning operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
How automated can a mushroom canning factory realistically be?
Does automation damage delicate mushrooms?
Is automation suitable for small or medium producers?
Which step should be automated first?
How does automation affect food safety audits?
Can automated lines handle multiple can sizes?
What is the typical lifespan of automated canning equipment?
Must-Read Blogs For Chain Restaurants Owner
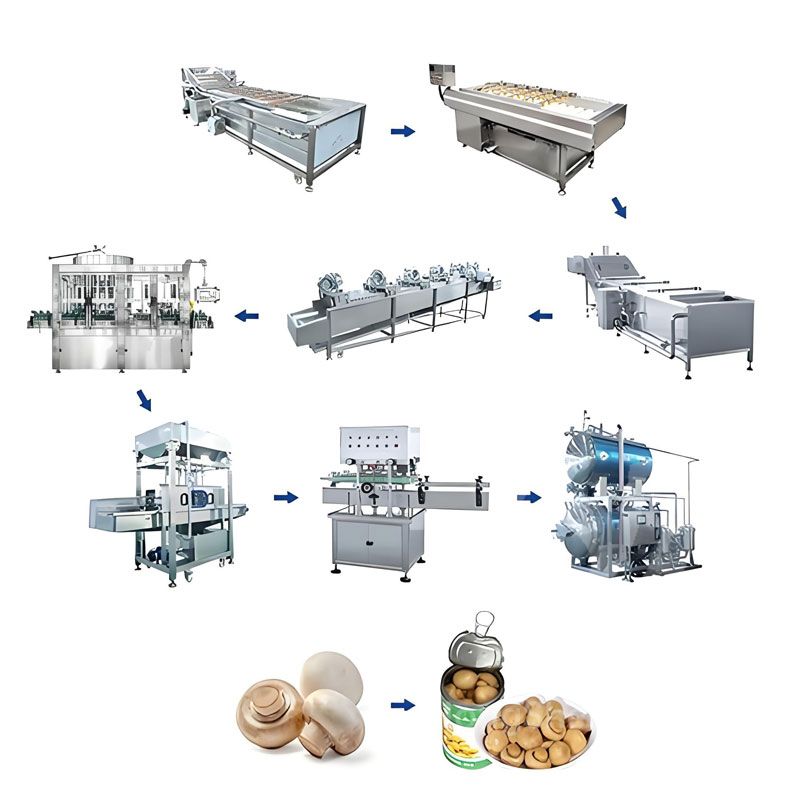






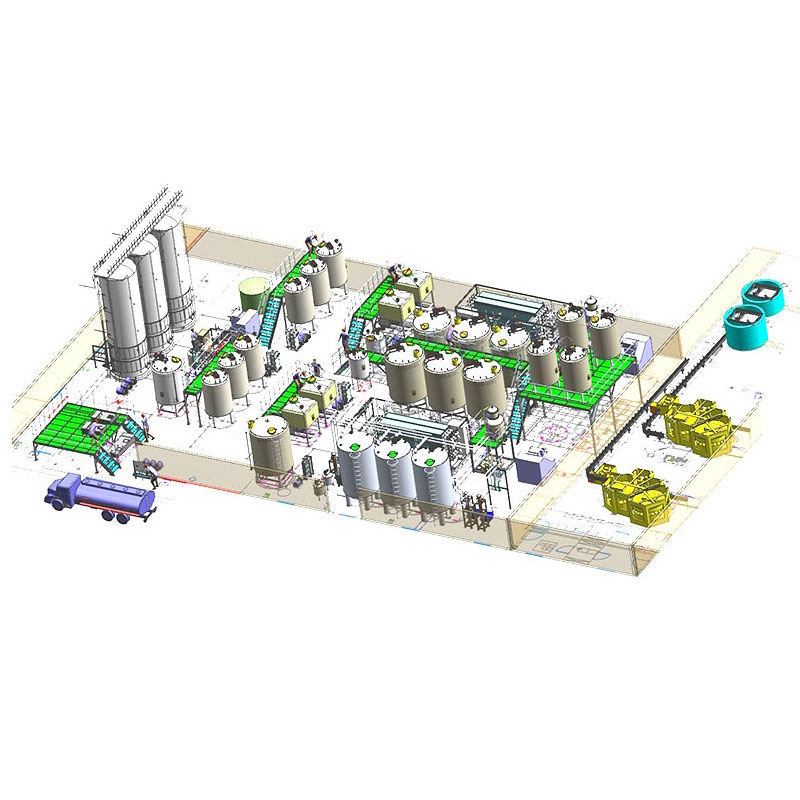



 Button Mushroom Canning Production Line
Button Mushroom Canning Production Line Cold Chain Rice Production Line
Cold Chain Rice Production Line Unmanned Intelligent Rice Production Line
Unmanned Intelligent Rice Production Line
Ready to Get Started?