What kind of equipment is needed for meat processing companies of different scales?
In the dynamic world of meat processing, having the right equipment is crucial for efficiency, quality, and safety. Whether you're running a small-scale butcher shop or managing a large industrial meat processing plant, your equipment needs will vary significantly. This comprehensive guide will explore the essential equipment required for meat processing companies of different scales, helping you make informed decisions for your business.
1. Introduction
The meat processing industry plays a vital role in the global food supply chain, transforming raw animal products into safe, edible, and marketable goods. The scale of operations can range from small local butcher shops to massive industrial facilities producing thousands of tons of meat products daily. Regardless of size, all meat processing companies require specialized equipment to ensure food safety, maintain product quality, and meet regulatory standards.
In this article, we'll break down the essential equipment needed for small, medium, and large-scale meat processing operations, along with crucial safety, sanitation, and packaging equipment. We'll also touch on recent technological advancements and provide guidance on choosing the right equipment for your business.
2. Small-Scale Meat Processing Equipment
Small-scale meat processors, such as local butcher shops or artisanal meat producers, require a core set of equipment to handle basic processing tasks. These typically include:
Cutting and Preparation Equipment
- Butcher blocks and cutting boards: High-quality, food-grade surfaces for cutting and preparing meat.
- Knives: A variety of professional-grade knives, including boning knives, cleavers, and trimming knives.
- Meat saws: Manual or electric saws for cutting through bones and frozen meat.
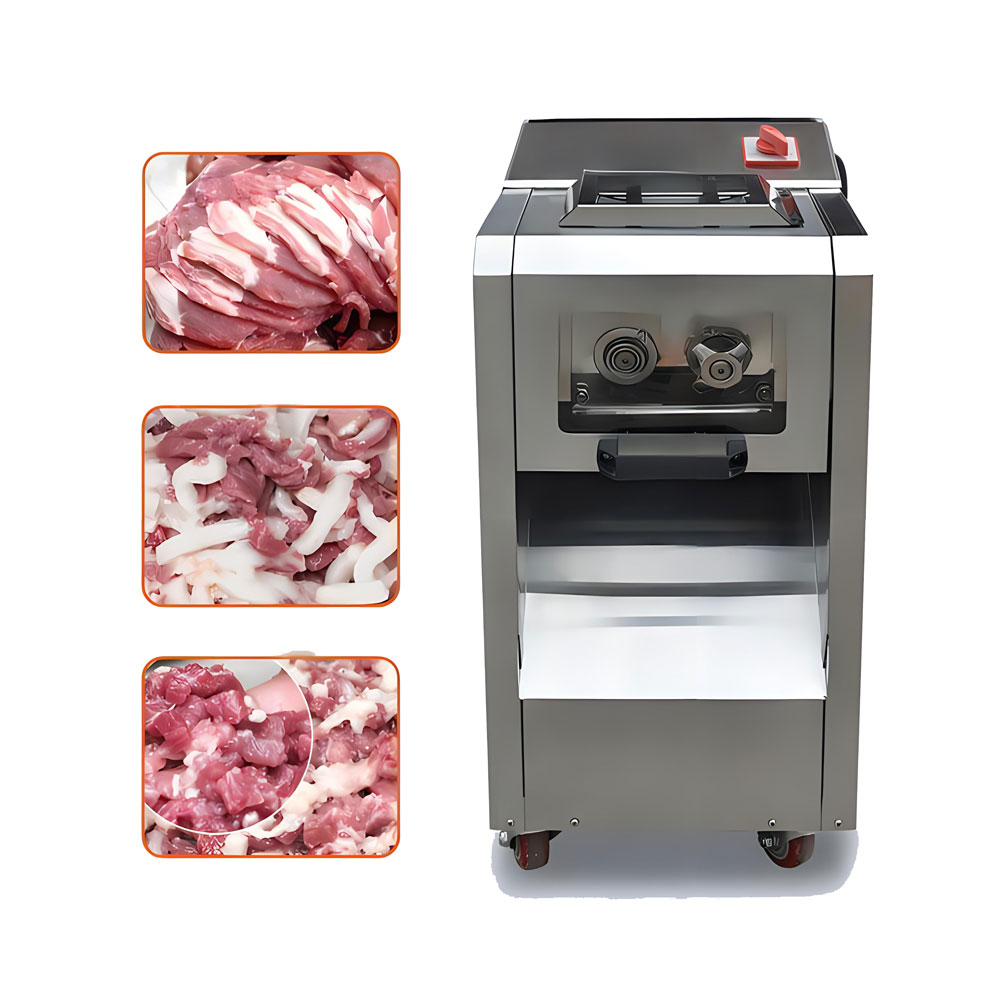
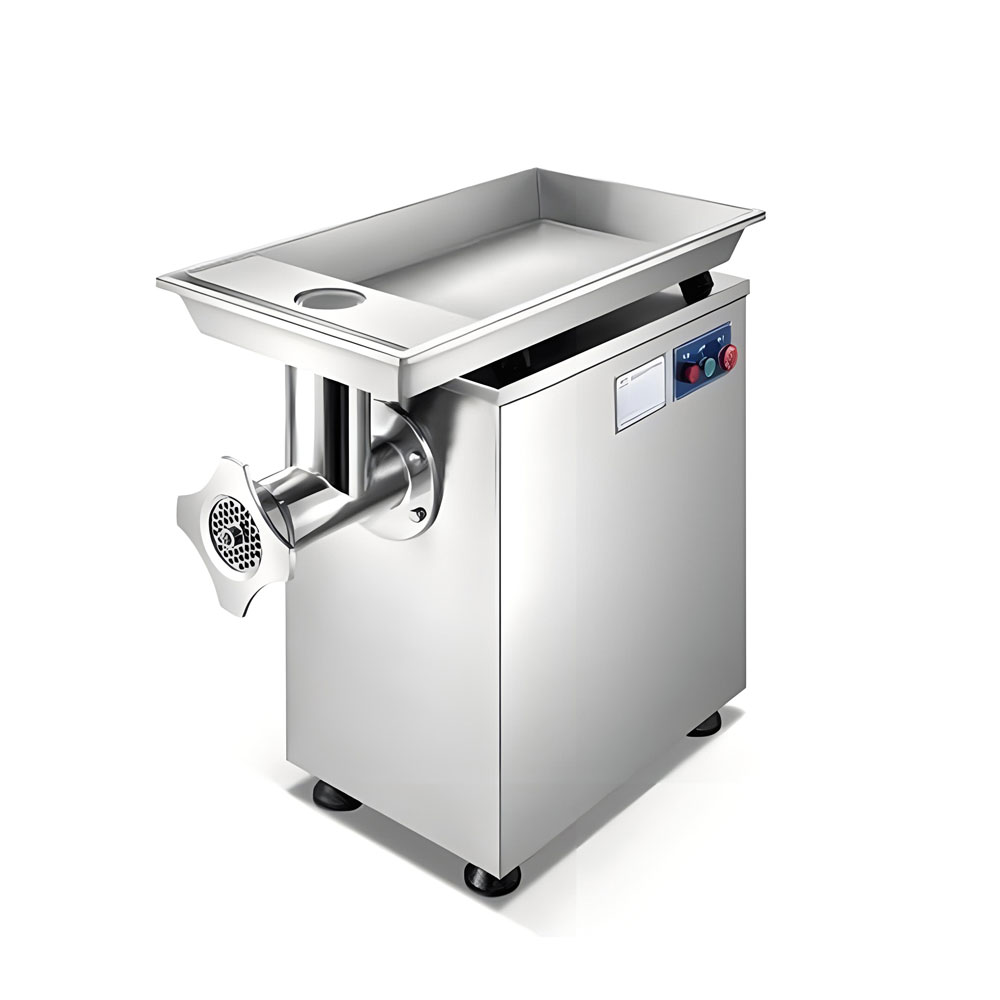
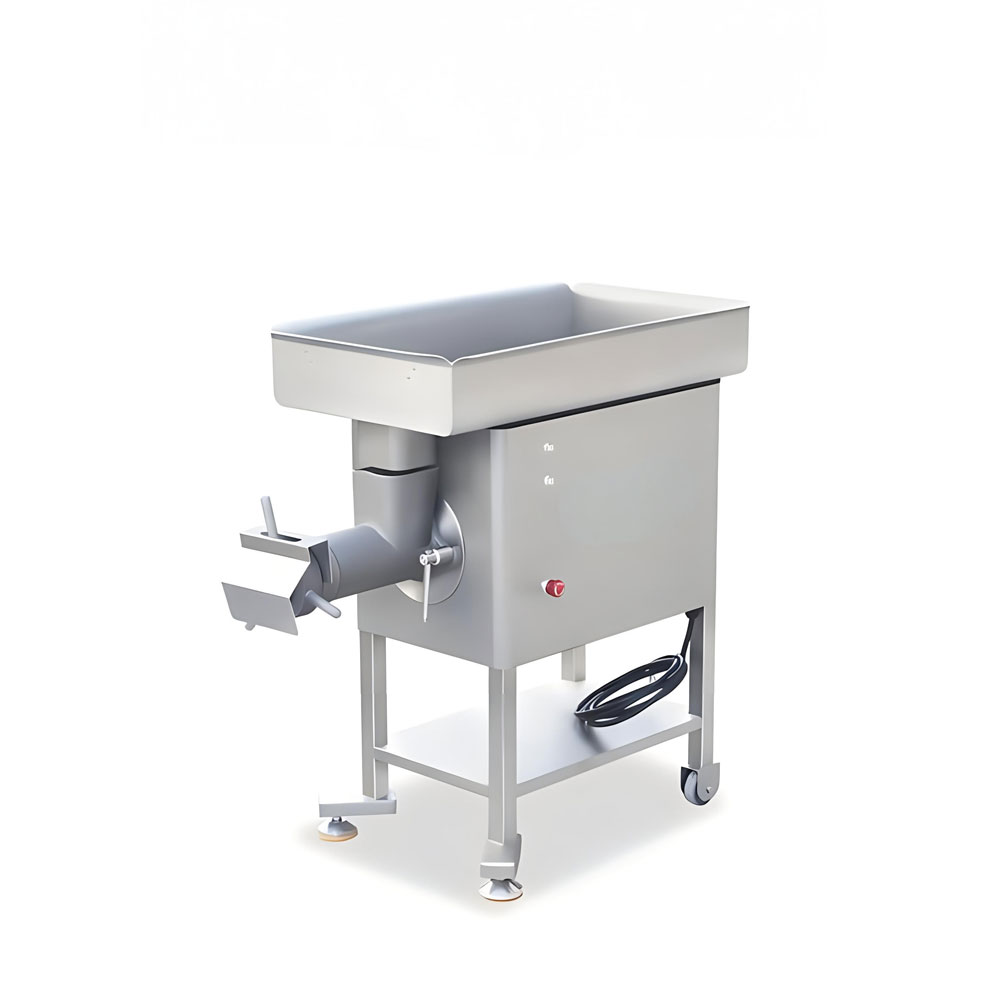
- Meat grinders: Small to medium-sized grinders for producing ground meat products.
Meat slicers: For creating uniform slices of various meats.
Processing Equipment
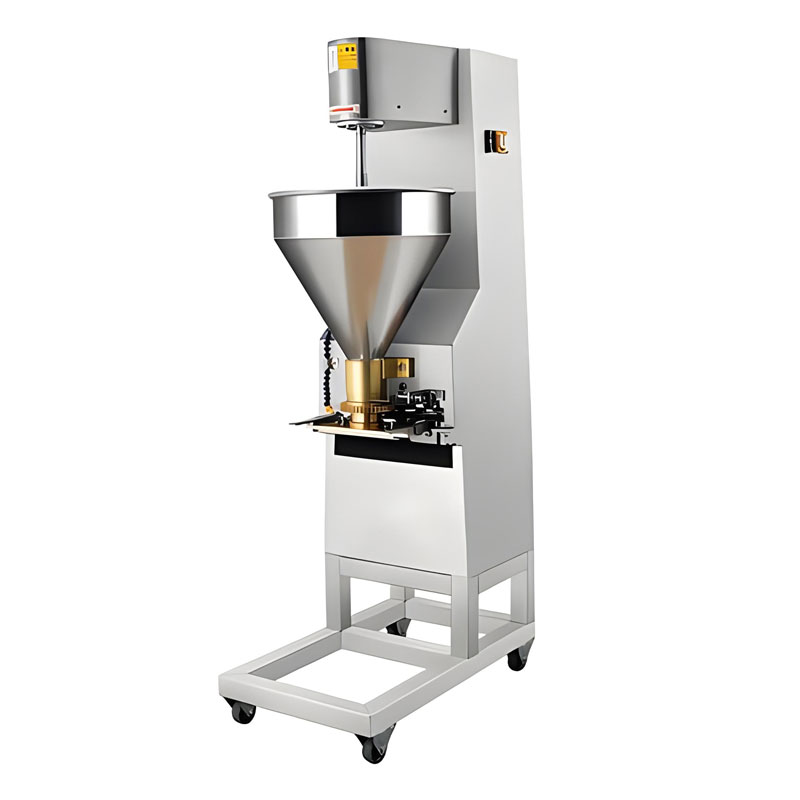
- Sausage stuffers: Manual or small electric stuffers for producing sausages and other encased products.
- Meat mixers: Small-capacity mixers for blending seasonings and creating consistent meat mixtures.
Tenderizers: Manual or small electric tenderizers to improve meat texture.
Weighing and Measuring
- Scales: Precise digital scales for portioning and pricing meat products.
- Thermometers: Instant-read thermometers for monitoring meat temperatures during processing and storage.
Basic Refrigeration
- Refrigerators and freezers: Small to medium-sized units for storing raw meat and finished products.
- Display cases: For showcasing products to customers in a retail setting.
3. Medium-Scale Meat Processing Equipment
As operations scale up, more specialized and higher-capacity equipment becomes necessary. Medium-scale processors, such as regional suppliers or larger butcher operations, typically require:
Advanced Cutting and Preparation
- Band saws: Larger, more powerful saws for efficient cutting of meat and bones.
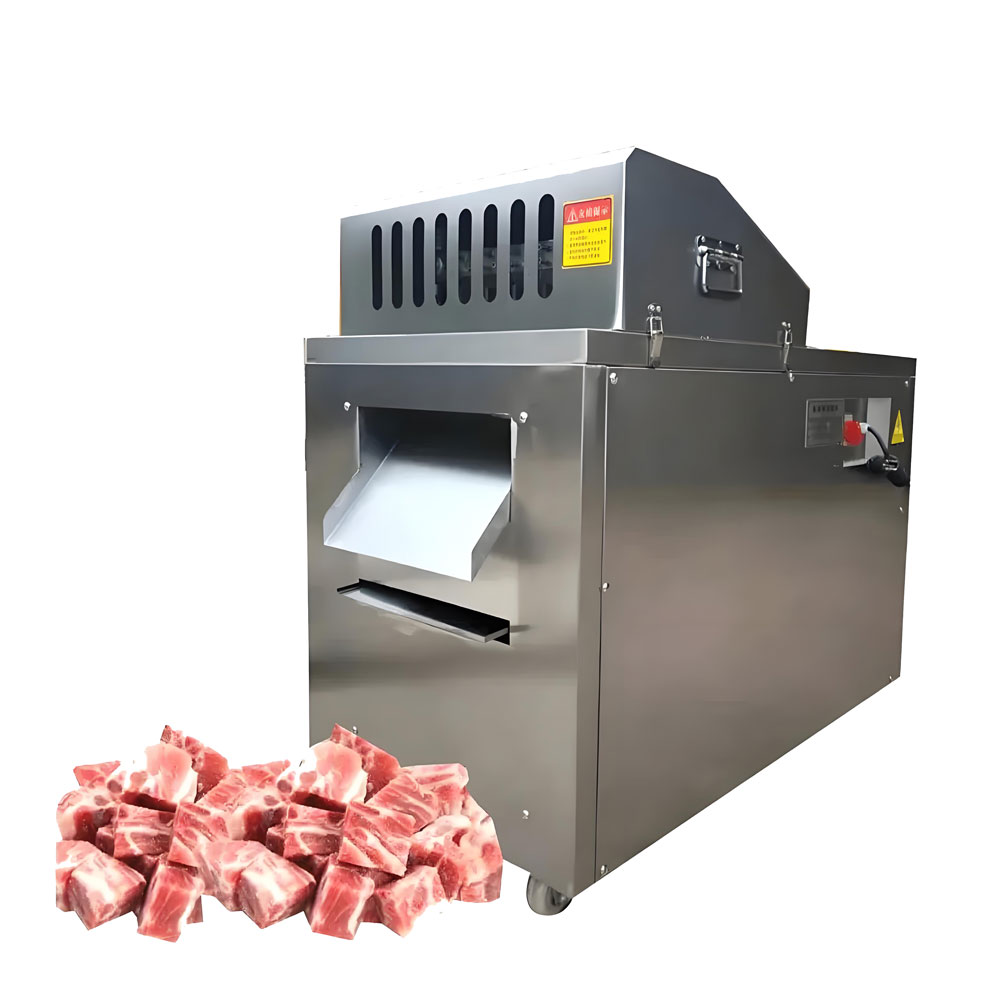
- Portion cutters: Automated machines for creating uniform portions of meat products.
- Dicer and cuber machines: For producing consistently sized meat cubes or strips.
Enhanced Processing Equipment
- Industrial meat grinders: Higher capacity grinders capable of processing larger volumes.
- Vacuum tumblers: For marinating and tenderizing meat products more efficiently.
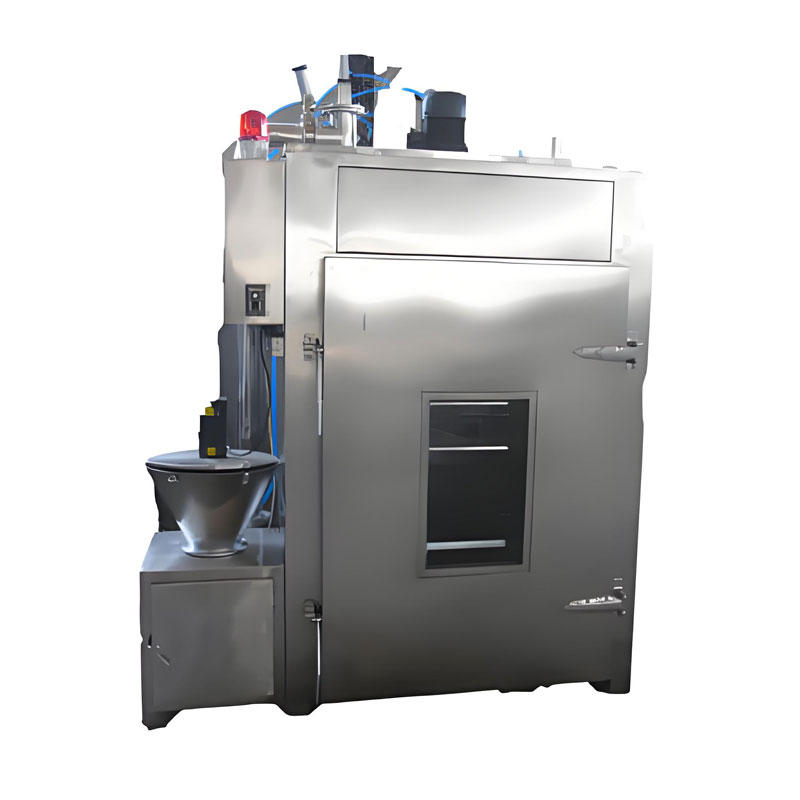
- Smokehouses: Small to medium-sized units for smoking and cooking meat products.
- Injectors: For adding brine, marinades, or other solutions to enhance flavor and texture.
Mixing and Blending
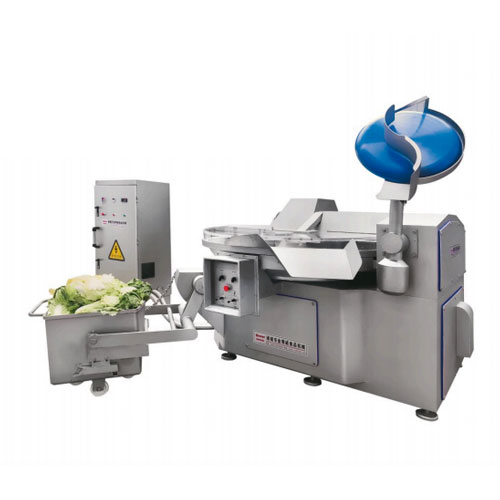
- Large-capacity meat mixers: For efficiently blending larger batches of ground meat or sausage mixtures.
- Emulsifiers: To create finely textured meat products like hot dogs or bologna.
Improved Refrigeration and Storage
- Walk-in coolers and freezers: For storing larger quantities of raw materials and finished products.
- Blast chillers: To rapidly cool cooked products, enhancing food safety and shelf life.
Packaging Equipment
- Vacuum packaging machines: For extending the shelf life of meat products.
- Labeling systems: To efficiently label products with necessary information.
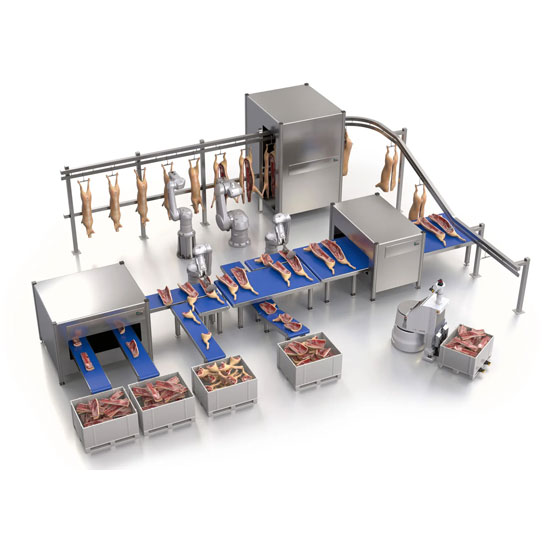
4. Large-Scale Industrial Meat Processing Equipment
Large-scale industrial meat processors require highly specialized, automated equipment to handle massive volumes efficiently. This equipment includes:
Advanced Slaughtering and Primary Processing
- Stunning equipment: Humane stunning systems for livestock.
- Overhead conveyor systems: For moving carcasses through various processing stages.
- Hide removal machines: Automated systems for efficiently removing animal hides.
- Carcass splitting saws: Powerful, automated saws for dividing carcasses.
High-Volume Cutting and Deboning
- Automated cutting lines: Computer-controlled systems for precise, high-speed cutting.
- Robotic deboning machines: For efficiently removing meat from bones.
- Water jet cutters: High-pressure water systems for precise meat cutting.
Large-Scale Processing Equipment
- Industrial-sized grinders and emulsifiers: Capable of processing tons of meat per hour.
- Continuous thermal processing systems: For cooking large volumes of meat products.
- Large-scale smokehouses and ovens: For smoking and cooking meat products in bulk.
High-capacity mixers and blenders: For preparing large batches of seasoned or mixed meat products.
Advanced Packaging Systems
- High-speed packaging lines: Automated systems for packaging various meat products.
- Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) equipment: For extending product shelf life.
- Shrink wrapping and sealing machines: For efficient packaging of large quantities.
Specialized Refrigeration and Storage
- Large-scale cold storage facilities: Including automated storage and retrieval systems.
- Spiral freezers: For rapid freezing of packaged meat products.
Refrigerated trucks and loading docks: For maintaining the cold chain during distribution.
5. Essential Safety and Sanitation Equipment
Regardless of scale, all meat processing operations must prioritize safety and sanitation. Essential equipment includes:
- Personal protective equipment (PPE): Including cut-resistant gloves, hairnets, and protective clothing.
- Handwashing stations: Strategically placed throughout the facility.
- Sanitizing equipment: Including foamers, sprayers, and automated cleaning systems.
- Waste management systems: For proper disposal of meat by-products and waste.
- Metal detectors: To ensure no metal contaminants are present in final products.
- Air purification systems: To maintain air quality and reduce odors.
6. Packaging and Storage Equipment
Proper packaging and storage are crucial for maintaining product quality and safety:
- Vacuum packaging machines: From small countertop units to large, automated systems.
- Tray sealers: For retail-ready packaging of fresh meat products.
- Labeling systems: To provide necessary product information and traceability.
- Cold storage units: Ranging from small refrigerators to large cold rooms and freezers.
- Temperature monitoring systems: To ensure proper storage conditions are maintained.
7. Technological Advancements in Meat Processing Equipment
The meat processing industry is continually evolving, with new technologies enhancing efficiency, safety, and quality:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: For optimizing cutting patterns and reducing waste.
- Internet of Things (IoT) sensors: For real-time monitoring of equipment performance and product quality.
- 3D imaging and X-ray technology: For non-invasive quality assessment and contaminant detection.
- Robotics: Increasingly used for tasks like sorting, picking, and packaging.
- Blockchain technology: For enhancing traceability throughout the supply chain.
8. Choosing the Right Equipment for Your Business
When selecting equipment for your meat processing operation, consider the following factors:
- Scale of operations: Choose equipment that matches your current production volume with room for growth.
- Budget: Balance initial costs with long-term efficiency and durability.
- Product range: Ensure your equipment can handle the types of meat products you plan to produce.
- Regulatory compliance: Verify that all equipment meets relevant food safety standards and regulations.
- Energy efficiency: Consider the long-term operational costs, including energy consumption.
- Maintenance and support: Look for equipment with good warranty coverage and readily available technical support.
- Integration: Ensure new equipment can integrate seamlessly with your existing processes and systems.
- Scalability: Choose equipment that can adapt to your business growth and changing market demands.
9. Conclusion
The right equipment is the backbone of any successful meat processing operation, regardless of its scale. From small butcher shops to large industrial facilities, having the appropriate tools and machines ensures efficiency, product quality, and food safety. As technology continues to advance, staying informed about the latest equipment innovations can give your business a competitive edge.
Whether you're just starting out or looking to upgrade your existing operations, carefully assess your needs, budget, and long-term goals when selecting meat processing equipment. By investing in the right equipment, you'll be well-positioned to meet the demands of your customers and thrive in the dynamic meat processing industry.
Remember, the key to success lies not just in having the right equipment, but also in maintaining it properly, training your staff effectively, and continuously adapting to industry trends and consumer preferences. With the right approach and equipment, your meat processing business can achieve new heights of productivity, quality, and success.
Must-Read Blogs For Chain Restaurants Owner















 Aseptic Canning Production Line Equipment
Aseptic Canning Production Line Equipment Sweet Corn Canning Production Line
Sweet Corn Canning Production Line Egg Canning Production Line
Egg Canning Production Line Canned Fruit Production Line Equipment
Canned Fruit Production Line Equipment
Ready to Get Started?